Die casting molds function as precision-engineered tools utilizing complex components, rigorous design principles, and distinct configurations to shape molten metal into durable parts. You likely face a familiar manufacturing nightmare where production lines halt because a tool failed unexpectedly or parts arrived with defects. 30 seconds too long in cycle time or a single porosity issue ruins your profit margins instantly. We eliminate this risk by deploying a high-performance aluminum die casting mould designed for speed and longevity.
How does the casting process actually work?
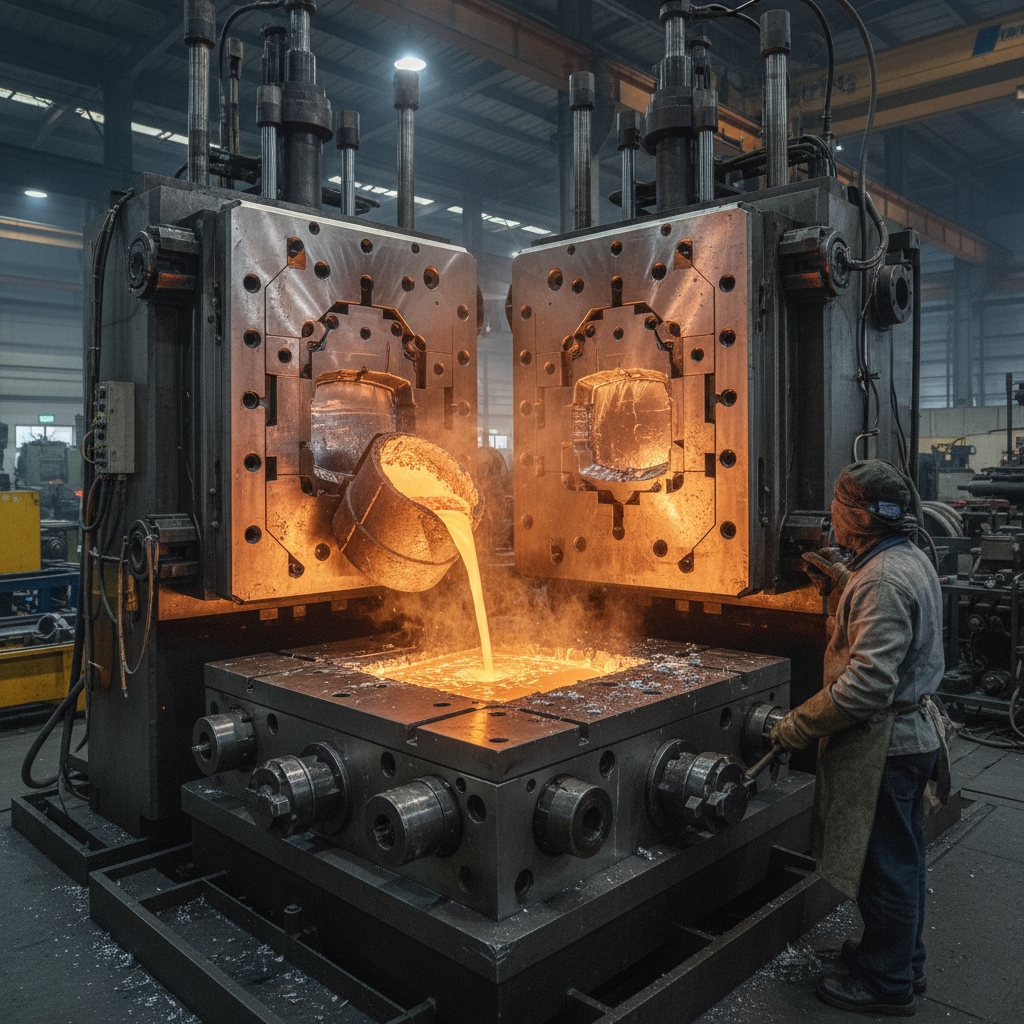

Casting transforms raw ingots into complex geometries through high-pressure injection. Molten metal enters a steel shot sleeve before a plunger forces it into a sealed cavity at incredible speeds. This mechanism fills intricate details instantly while trapping minimal air. Here represents the core of modern manufacturing efficiency.
You might be wondering how pressure affects the outcome. High intensification pressure squeezes the metal during solidification. This action reduces internal porosity while ensuring a dense final structure.
The injection phase explained
- Clamping: The machine locks die halves with immense tonnage.
- Injection: A plunger pushes metal into the cavity rapidly.
- Cooling: Metal solidifies within seconds inside the tool.
- Ejection: Pins push the casting out for finishing.
The process relies on synchronization. If the plunger moves too slowly, the metal freezes prematurely. Moving too fast causes turbulence. Finding this balance guarantees consistent part quality.
Solidification and ejection basics
Once filled, the metal must cool uniformly to maintain dimensional stability. The machine holds pressure until the part becomes rigid enough for removal. But here’s the thing. Ejection must happen immediately after solidification to prevent shrinking metal from gripping the steel tool.
Key TakeawayUnderstanding process mechanics allows you to optimize cycle times effectively. A well-calibrated injection phase reduces scrap rates significantly while boosting daily output.
| Parameter | Impact on Quality | Ideal State | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Speed | Surface finish | Fast fill without turbulence | |
| Holding Pressure | Part density | High enough to compress gas | |
| Cooling Time | Cycle efficiency | Minimal required for rigidity |
Analyze your current cycle parameters to identify where seconds can be shaved off without compromising integrity.
What components make up the mold assembly?
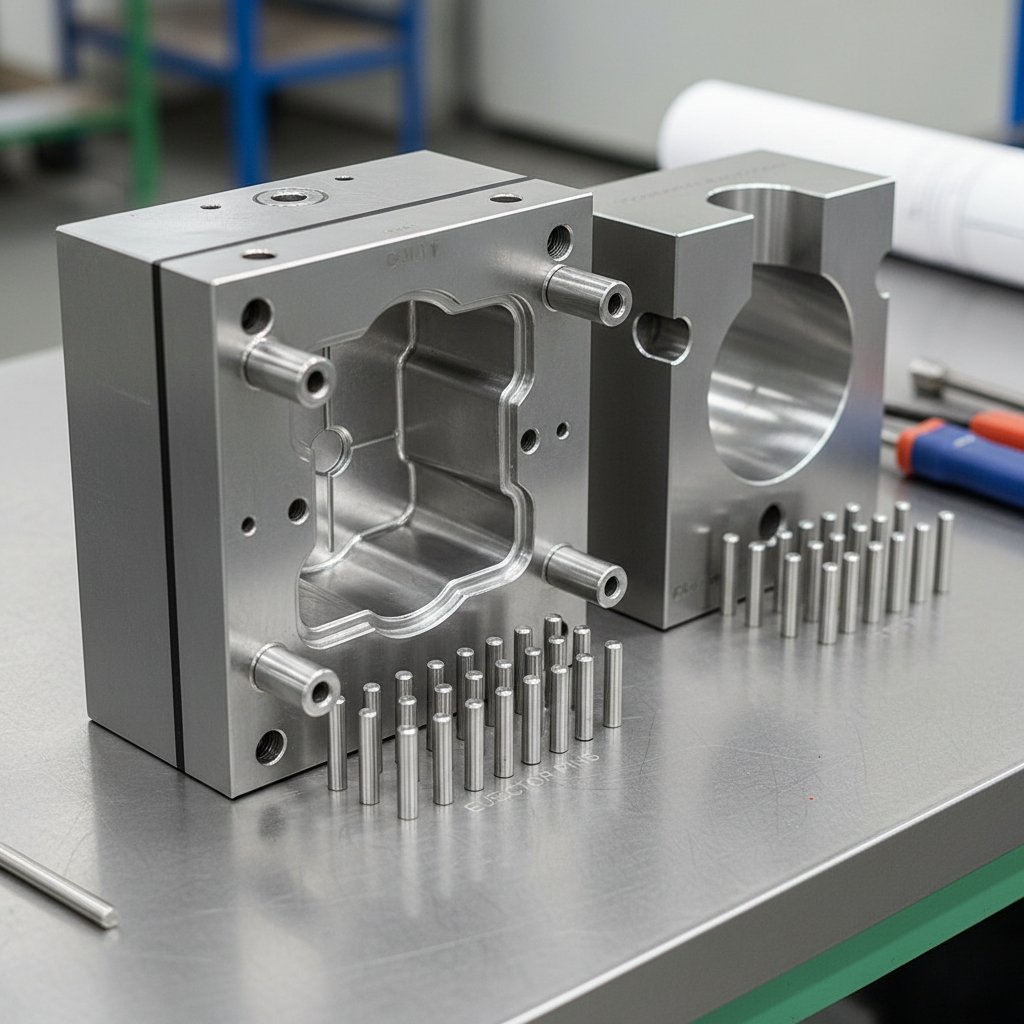
A mold serves as a complex assembly rather than a simple block of steel. The fixed half attaches to the machine platen while the moving half contains the ejection system. This is where it gets interesting. Every investment casting tooling component must align within microns to prevent flash.
Core slides allow for undercuts or side holes. Without these moving parts, creating complex geometries becomes impossible. These mechanisms add cost but enable sophisticated design features.
Why are cores and cavities vital?
- Cavity: Forms the exterior cosmetic surface.
- Core: Creates internal features and structural ribs.
- Slides: Enable side-action geometry creation.
Cores experience the highest thermal stress. They are surrounded by molten metal during every shot. Selecting premium steel for these inserts prevents early heat checking.
The role of ejector pins
Pins push the part out of the moving die half. Placing them incorrectly leaves witness marks on critical cosmetic surfaces. Imagine this scenario. A pin pushes too hard on a hot part and punctures it.
Key TakeawayKnowing your components helps in troubleshooting specific defects. Identifying whether a core pin or an ejector causes an issue saves valuable maintenance hours.
| Component | Primary Function | Common Failure Mode | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Die | Stationary molding surface | Thermal fatigue cracking | |
| Moving Die | Ejection side housing | Guide pillar wear | |
| Slides | Side feature creation | Seizing due to friction |
Inspect your wear plates and guide pins monthly to prevent catastrophic assembly seizure.
How do you navigate the design process?
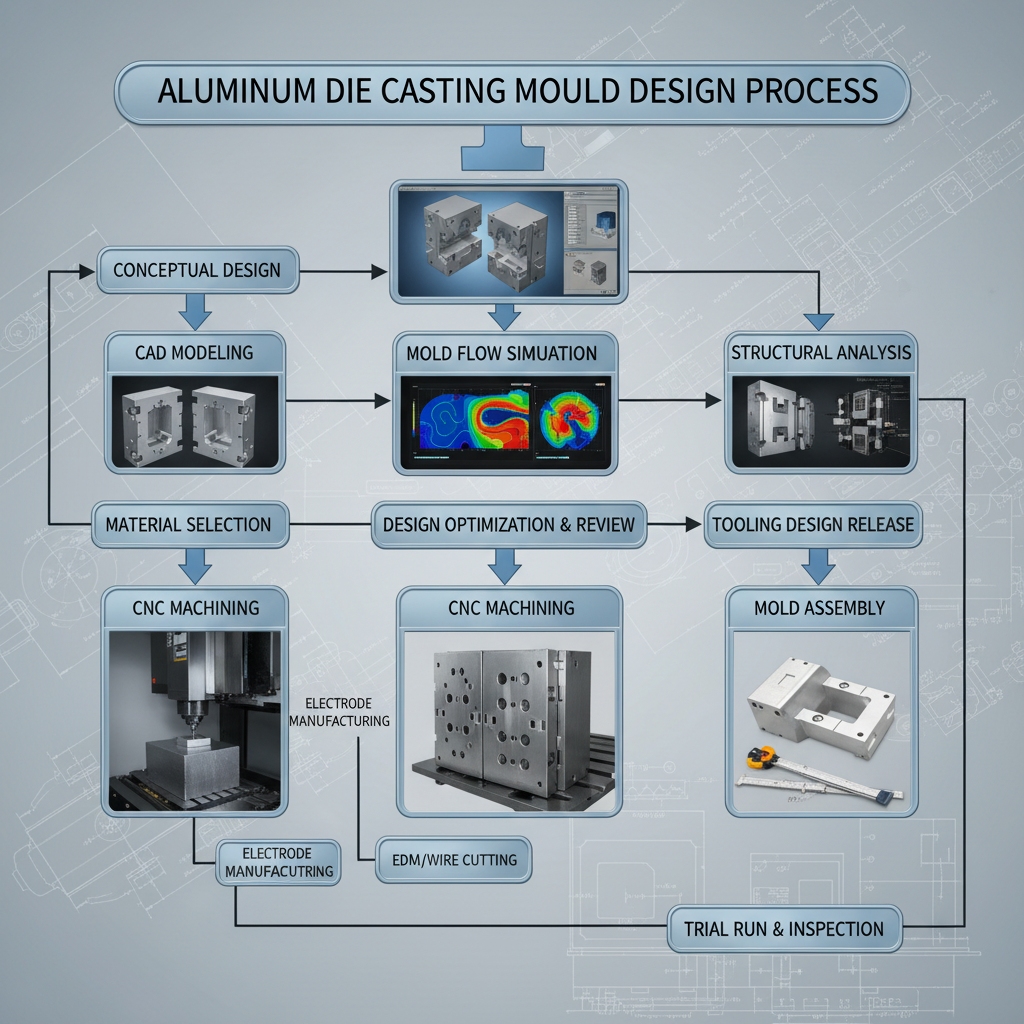
Design determines destiny in manufacturing. Engineers utilize CAD software to model part geometry while adding draft angles for easy release. Ready for the good part? Simulation software predicts flow patterns before cutting any steel.
Ignoring draft angles guarantees parts will stick. A minimum of 1-2 degrees ensures the casting releases smoothly from the cavity. This simple addition prevents production stoppages.
Simulation and flow analysis
- Fill Time: Visualizes how fast metal fills the cavity.
- Thermal Map: Identifies hot spots causing warpage.
- Air Entrapment: Predicts where porosity might occur.
Engineers use these insights to adjust gate locations. Moving a gate just a few millimeters can eliminate air pockets completely.
Draft angles and shrinkage
Metal shrinks as it cools. Design must account for this by making the mold cavity slightly larger than the final part. Here represents a critical fact. Different alloys shrink at different rates.
Key TakeawayInvest time in the design phase to avoid costly rework later. Simulation identifies problems virtually so you never face them physically.
| Design Step | Purpose | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Draft Analysis | Ensure ejection | Prevents stuck parts | |
| Flow Simulation | Optimize filling | Reduces porosity | |
| Shrinkage Calc | Dimensional accuracy | Meets tolerance specs |
Review your flow analysis reports before approving any final tool design.
Which steel grades determine tool longevity?
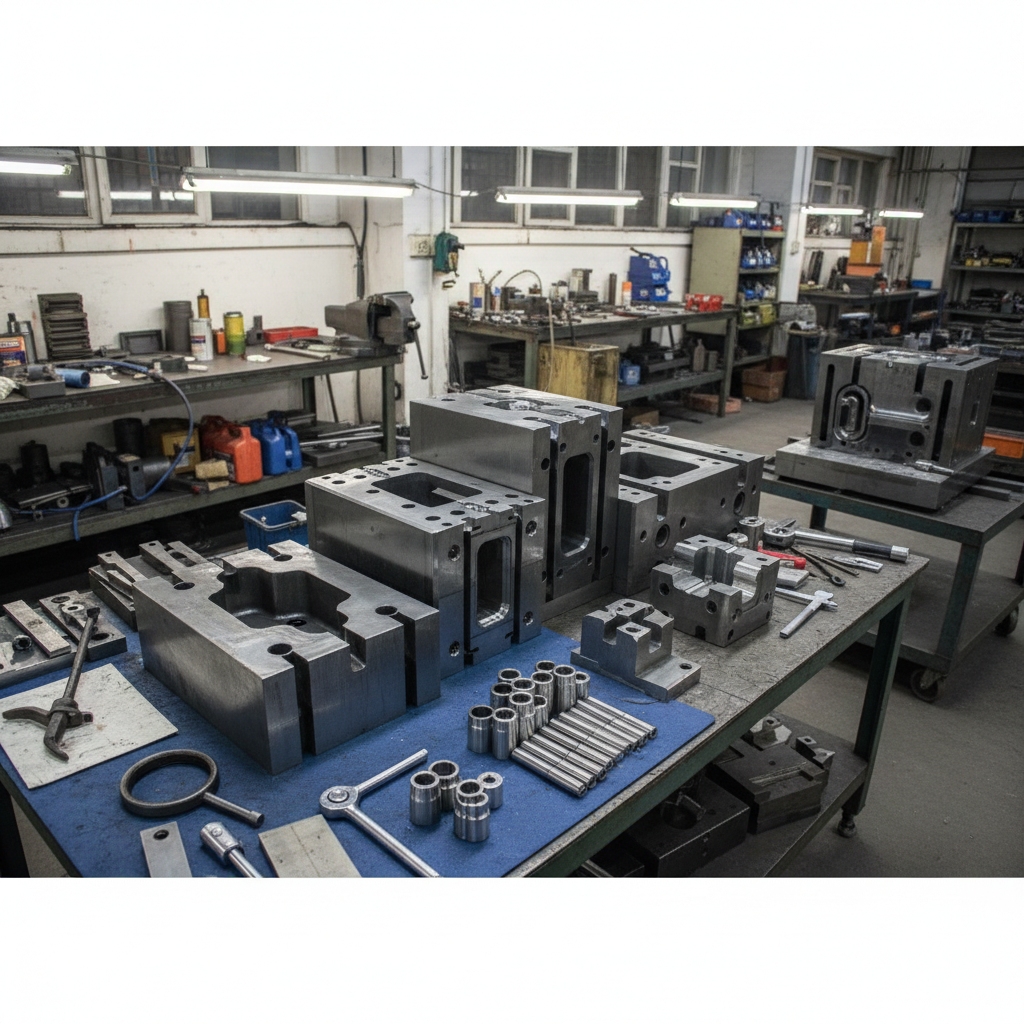

Material selection dictates how long a tool lasts. H13 hot-work tool steel remains the industry standard for aluminum applications due to high toughness. Wait until you hear this. Premium grades like DIEVAR offer superior resistance to heat checking.
Choosing cheaper steel saves money upfront but costs more long-term. Low-grade steel cracks after fewer cycles, forcing early replacement.
Standard steel options
- H13: Excellent balance of toughness and heat resistance.
- P20: Used for zinc or low-volume prototypes.
- Maraging Steel: Highest strength for critical core pins.
Heat treatment hardens the steel surface. This process creates a durable skin capable of withstanding erosion from high-velocity molten metal.
Heat treatment benefits
Proper tempering relieves internal stress. A material testing regimen ensures the steel reaches the correct hardness (46-48 HRC) without becoming brittle.
Key TakeawaySelecting the right steel grade aligns tool life with project volume. Premium steel is an investment in uninterrupted production runs.
| Steel Grade | Hardness (HRC) | Best Application | |
|---|---|---|---|
| H13 Standard | 46-48 | General aluminum production | |
| Premium H13 | 48-50 | High-volume cosmetic parts | |
| 2344 ESR | 48-52 | Complex cores and slides |
Verify material certification certificates to ensure you receive the steel grade specified.
Why is thermal regulation critical for success?
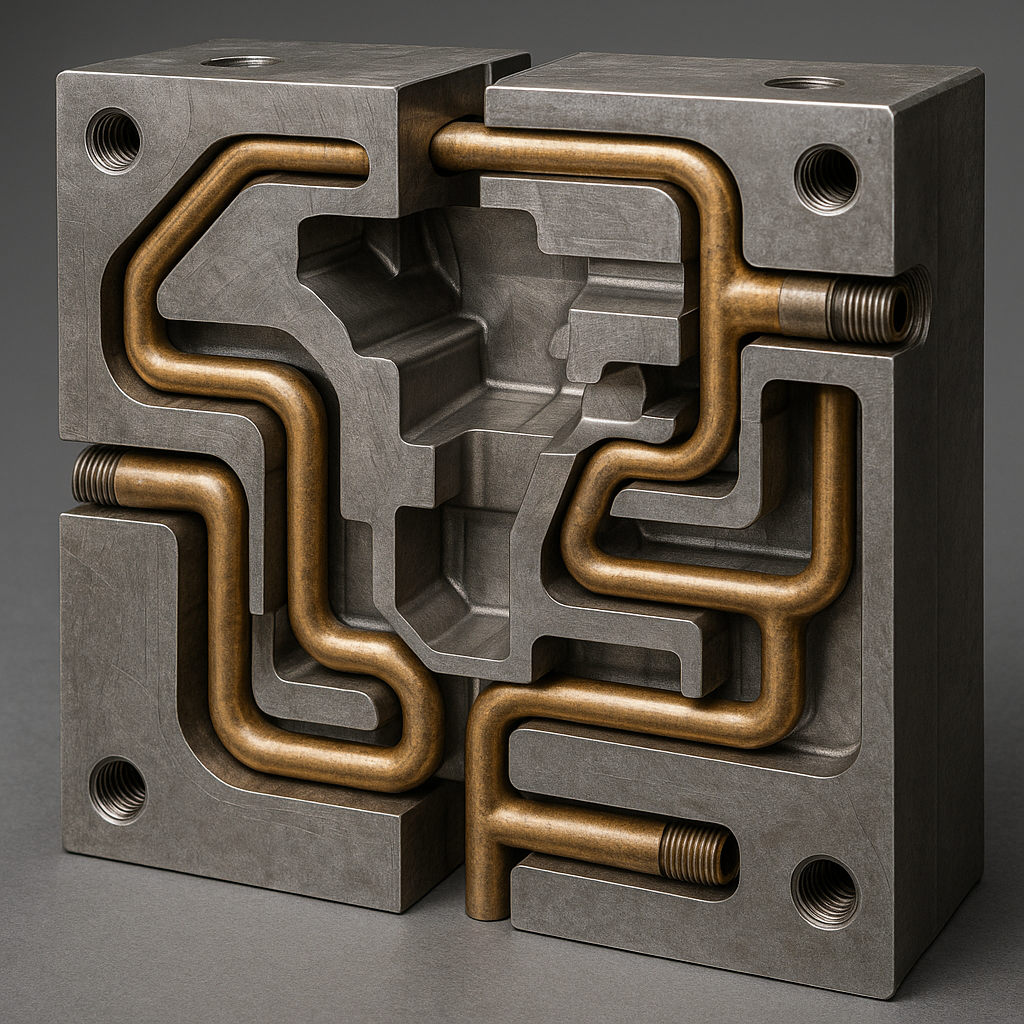
Managing heat defines cycle speed. Internal channels circulate oil or water to extract heat from molten metal rapidly. But here is the kicker. Uneven cooling causes parts to warp.
If one side cools faster, internal stresses pull the part out of tolerance. Balanced thermal regulation keeps dimensions stable shot after shot.
Managing thermal shock
- Oil Heating: Maintains die temp during breaks.
- Water Cooling: Rapidly removes heat during production.
- Spot Cooling: Targets thick sections specifically.
Cold starts destroy molds. Pre-heating the tool reduces the thermal shock experienced when hot metal hits cold steel.
Conformal cooling channels
Advanced manufacturing allows cooling lines to follow complex part curves. This changes everything. It reduces cycle time by accessing hard-to-reach areas.
Key TakeawayEfficient cooling systems drive profitability by reducing cycle times. A balanced thermal profile ensures parts remain straight and dimensionally accurate.
| Cooling Type | Efficiency | Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Straight Lines | Moderate | Low | |
| Baffled Lines | High | Medium | |
| Conformal | Very High | High |
Monitor your return water temperature to detect blocked cooling lines early.
How do gating and venting impact quality?
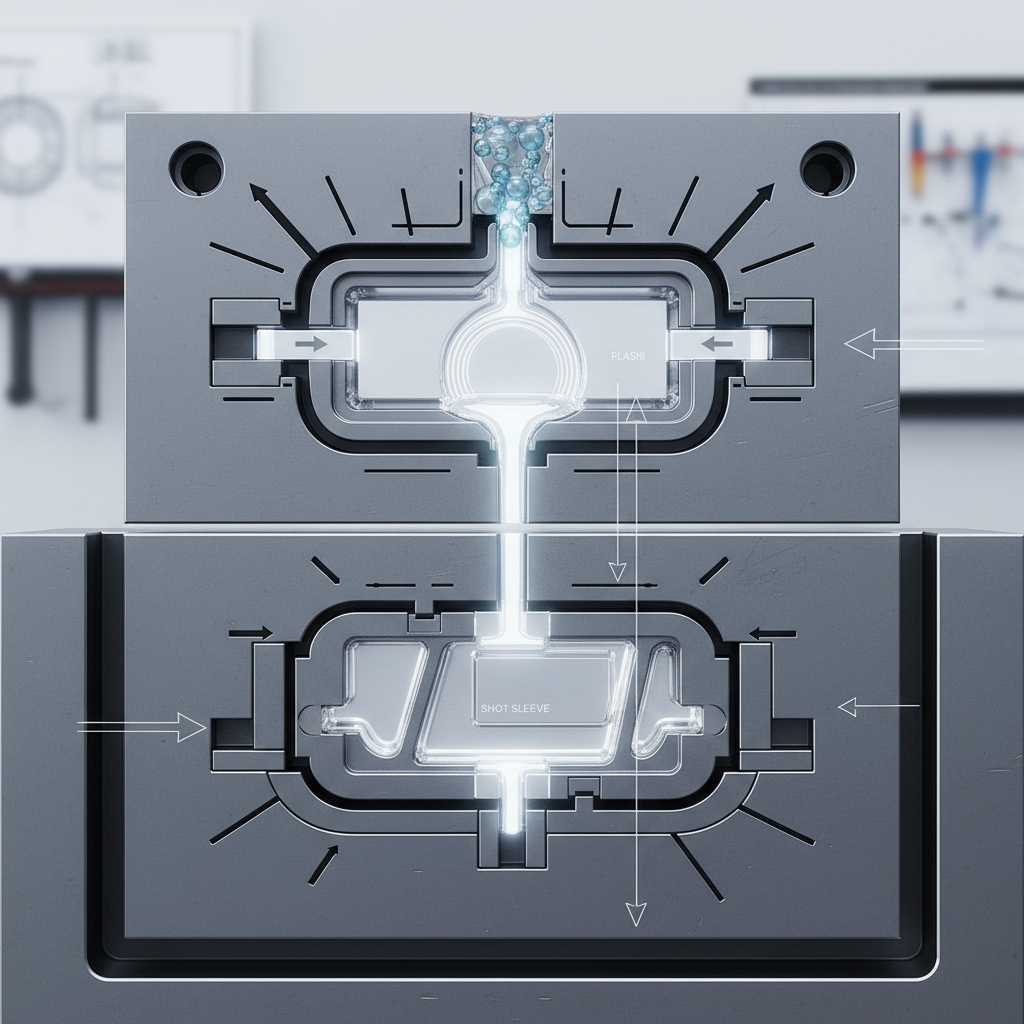
Getting metal in and air out requires precision. The gate controls velocity while vents allow gas escape. Here is the real story. Poor venting leads to gas porosity that weakens the part.
The runner system guides metal from the biscuit to the gate. It must minimize turbulence to prevent air mixing with the melt.
Designing the runner system
- Runner Area: Must decrease progressively towards the gate.
- Gate Velocity: Controlled to prevent erosion.
- Overflows: Capture the first (dirty) metal injected.
Overflows act as trash cans for oxides. They also provide extra heat to cold areas of the die.
Preventing air entrapment
Vacuum valves suck air out just before injection. This creates a vacuum within the cavity, allowing for denser parts suitable for heat treatment.
Key TakeawayProper gating and venting solve 90% of surface defects. Strategic placement ensures clean metal fills critical areas while air escapes freely.
| Feature | Function | Poor Design Result | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Runner | Transport metal | Turbulence / Air mixing | |
| Gate | Control flow | Surface erosion | |
| Vent | Exhaust air | Gas porosity bubbles |
Check vents for clogging after every shift to maintain consistent part density.
How can you extend your tooling lifespan?
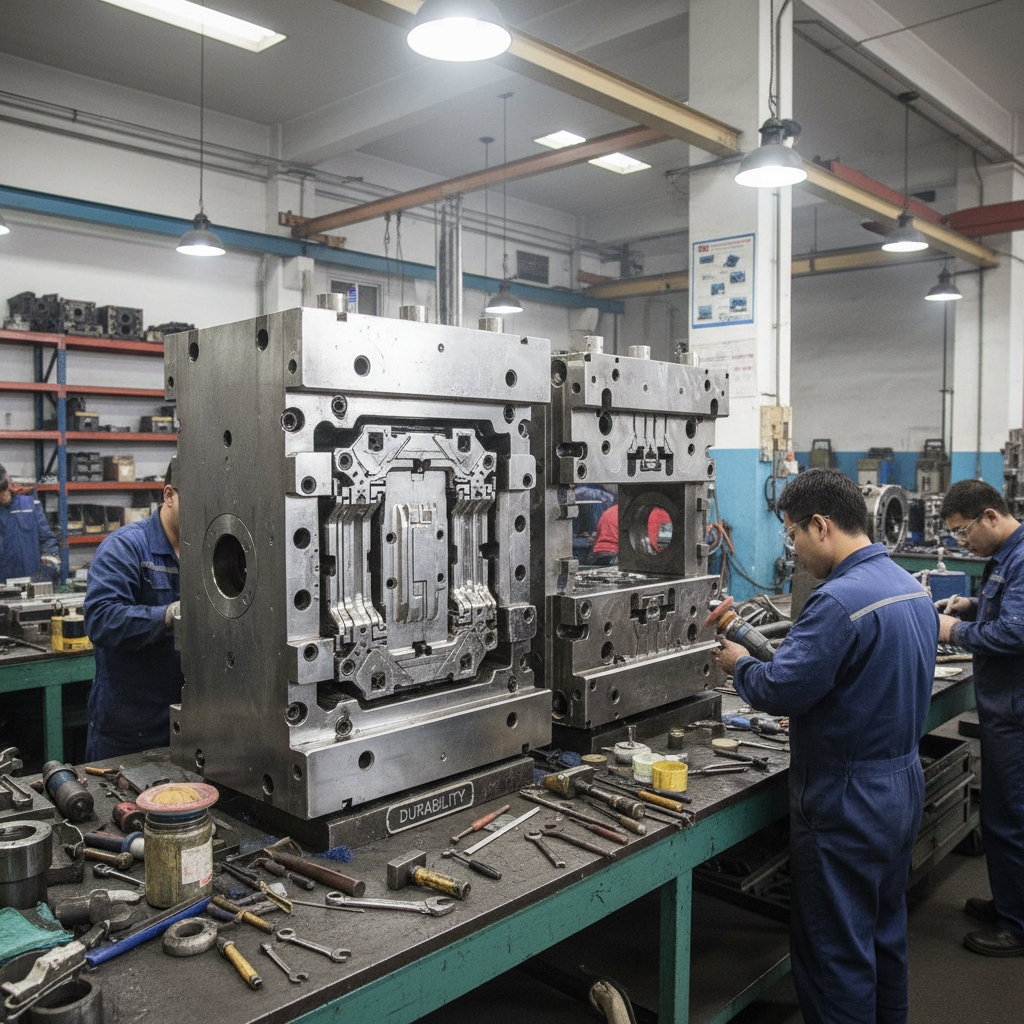

Molds degrade with every shot. Regular maintenance prevents minor wear from becoming major failure. Make no mistake. A dirty mold produces scrap.
Aluminum solder builds up on the cavity surface. Chemical cleaning removes this buildup without damaging the steel substrate.
Routine cleaning protocols
- Daily: Clean parting lines and vents.
- Weekly: Inspect cooling lines for leaks.
- Monthly: Check ejector pins for wear.
Applying proper release agents protects the steel. This barrier prevents soldering while aiding part release.
Stress tempering cycles
Steel accumulates stress from thermal cycling. Periodic stress tempering relaxes the material structure. Casting heat treatment expertise applies to tools as well as parts.
Key TakeawayProactive maintenance costs far less than emergency repairs. A strict cleaning schedule preserves critical surfaces and tolerances.
| Action | Frequency | Prevents | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parting Line Clean | Daily | Flash buildup | |
| Stress Temper | Every 5k shots | Heat check cracking | |
| Pin Lubrication | Weekly | Seized ejectors |
Implement a logbook for every tool to track shots and maintenance intervals.
Single cavity or multi-cavity: Which fits?

Volume requirements dictate cavity count. A single-cavity tool costs less but produces fewer parts. Think about this. Multi-cavity tools increase output but require larger machines.
Unit dies offer a middle ground. You change only the insert while keeping the master holder, reducing tooling costs for lower volumes.
Benefits of single cavity tools
- Lower Cost: Less machining and steel required.
- Better Control: Easier to optimize process parameters.
- Flexibility: ideal for large or complex parts.
Large automotive structural parts typically use single cavity molds. The sheer size prohibits multiple cavities.
When to choose multi-cavity
High-volume small parts demand multi-cavity solutions. Producing four parts per cycle slashes piece price significantly.
Key TakeawayAlign cavity count with your annual volume projection. Contacting a partner for machinery parts consultation helps define the best strategy.
| Mold Type | Volume Suitability | Tooling Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Cavity | Low – Medium | Low | |
| Multi-Cavity | High | High | |
| Unit Die | Low | Lowest |
Calculate the break-even point between tool cost and piece price savings.
Where are these molds used in industry?
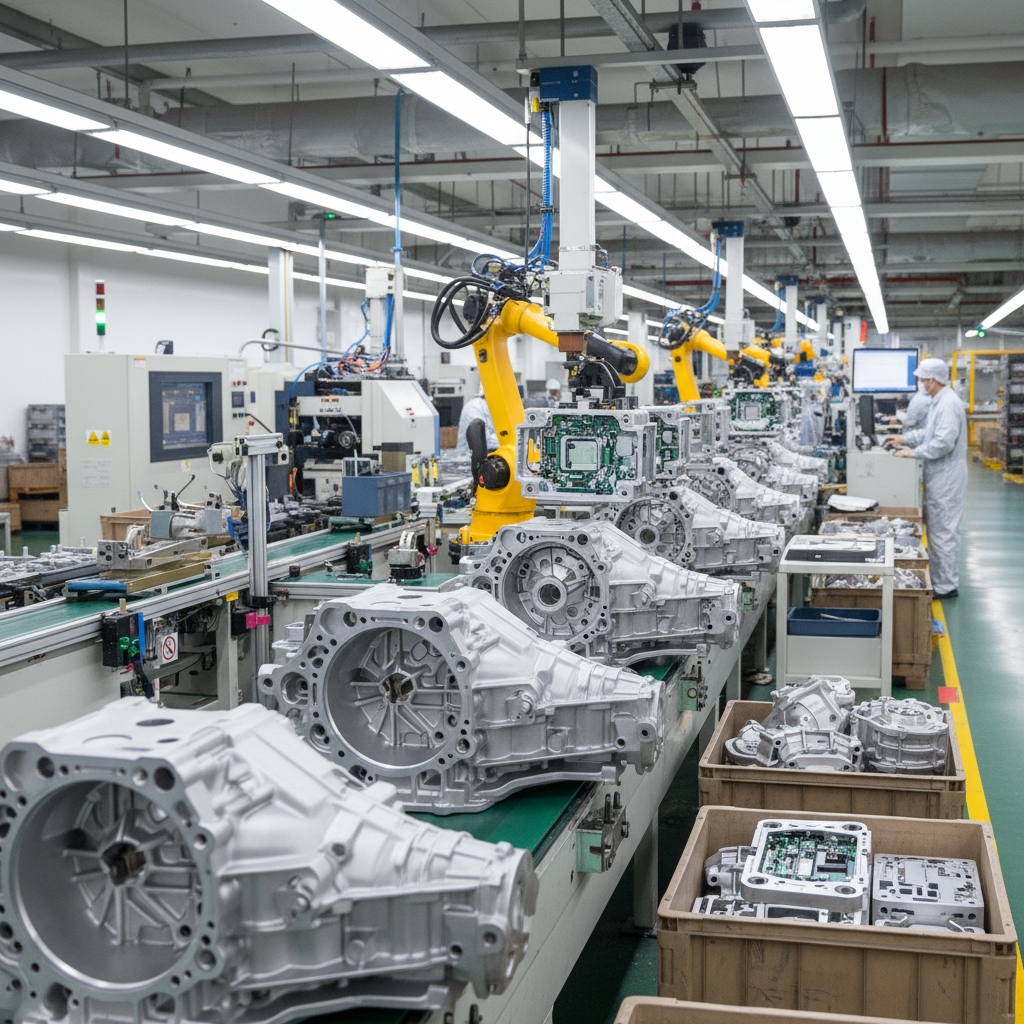

Every sector relies on die casting for robust metal parts. The automobile industry drives innovation with lightweight housings. It goes deeper. 5G infrastructure demands heat sinks with complex fins.
Medical devices require sterilizable metal components. Die casting offers the surface finish and durability needed for hospital environments.
Automotive and aerospace needs
- EV Battery Cases: Lightweight protection.
- Engine Brackets: High strength-to-weight ratio.
- Aerospace Fittings: Precision tolerance adherence.
Reducing weight increases fuel efficiency. Aluminum casting replaces heavy steel assemblies.
Consumer electronics housing
Laptops and cameras use thin-wall magnesium or aluminum castings. These provide EMI shielding that plastic cannot offer.
Key TakeawayDie casting versatility spans from heavy industry to delicate electronics. The process adapts to diverse requirements for strength, weight, and aesthetics.
| Industry | Key Part Types | Material Focus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Transmission / EV | A380 / ADC12 | |
| Telecom | Heat Sinks | A360 | |
| Consumer | Laptop Chassis | AZ91D (Magnesium) |
Review material properties to match the specific demands of your industry application.
How do we ensure mold precision and quality?
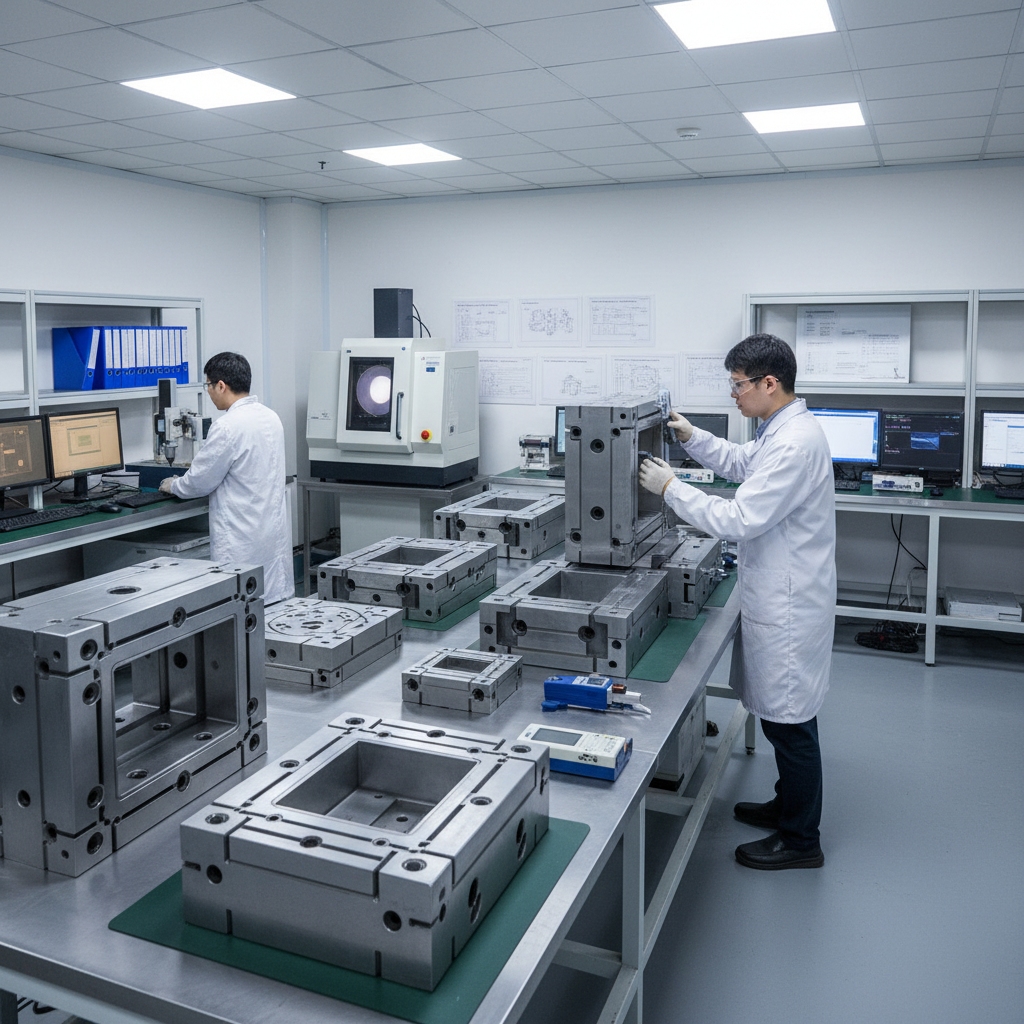

Quality assurance begins with the tool. Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) verify steel dimensions before production starts. You need to know this. Even a perfect mold produces bad parts if process control fails.
X-ray inspection sees inside the metal. It detects porosity invisible to the naked eye, ensuring structural integrity.
Advanced inspection methods
- CMM: Verifies dimensional accuracy.
- 3D Scanning: Compares physical part to CAD model.
- Spectroscopy: Confirms alloy chemical composition.
Routine checks catch wear trends. Measuring the last shot of a run predicts when maintenance becomes necessary.
Tolerance verification steps
Hardness testing confirms heat treatment success. Soft steel wears out rapidly, causing dimensional drift.
Key TakeawayRigorous quality control protects your reputation. Validating the tool and the process guarantees every shipment meets specifications.
| Method | Detects | Phase | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMM | Dimensional error | Setup / Production | |
| X-Ray | Internal porosity | Production | |
| Visual | Surface defects | Packing |
Establish a “first article” approval process to valid every production run start.
Conclusion
Mastering die casting molds requires balancing engineering precision with operational discipline. We explored how components interact, why material selection matters, and how maintenance safeguards your investment. You now possess the knowledge to make informed decisions about your tooling strategy. Empowering your production with precision and innovation remains our core mission. Do not let tooling failures slow you down. Contact us today to engineer your next success story.
FAQ
Can I modify a mold after it has been made?Modifying a mold involves risks. Removing steel to make a part feature larger is simple, but adding steel (welding) to make a feature smaller often compromises tool life and surface finish.
What is the best steel for high-volume aluminum runs?Premium H13 tool steel stands as the superior choice. It offers the best balance of toughness, thermal fatigue resistance, and machinability for high-pressure aluminum applications.
How often should I perform stress tempering?Stress tempering typically occurs every 3,000 to 5,000 shots initially. Doing this relaxes internal stresses caused by thermal cycling, significantly reducing the risk of catastrophic cracking.
Why do my parts have gas porosity?Trapped air or gas usually causes porosity. Inadequate venting, poor gate placement, or excessive injection plunger lubrication prevents air from escaping the cavity before the metal solidifies.
What is the typical lead time for a new mold?Lead times generally range from 4 to 8 weeks. Complexity, size, and current shop capacity influence this timeline, with design verification and simulation taking up the first week.
