Aluminum castings play a significant role across various industries, particularly in the automotive, packaging, and aerospace sectors. From lightweight rims to durable airplane parts, aluminum casting is an essential process that delivers reliable and high-performance components. This article delves into the fundamentals of aluminum castings, their applications, and the benefits they bring to industries worldwide. Let’s explore the manufacturing process, challenges, and how businesses can optimize their use of aluminum castings to improve operational efficiency and product quality.
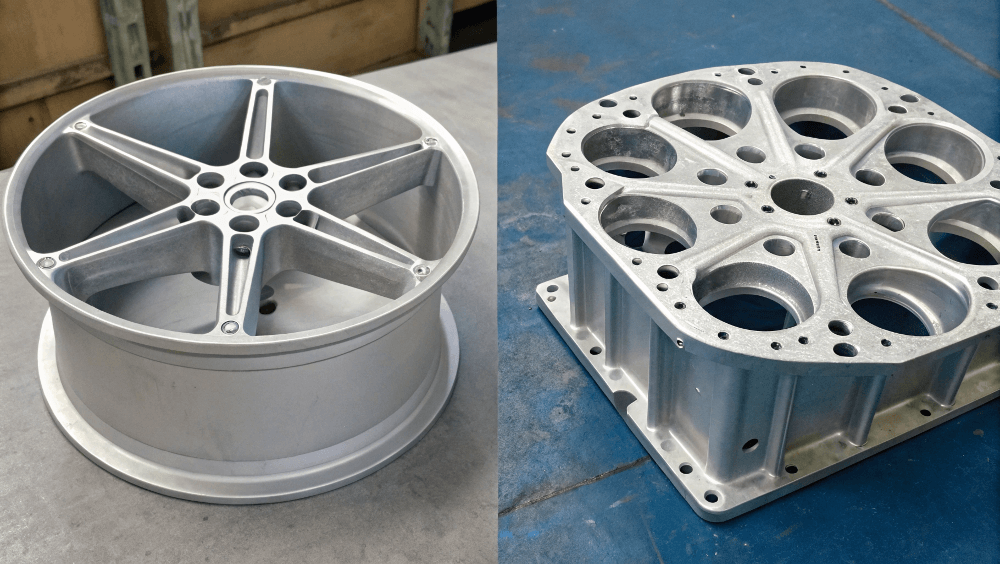
1. What are aluminum castings and why are they important?
Aluminum castings refer to components that are created by pouring molten aluminum into a mold, which then cools and solidifies into a desired shape. But here’s the kicker: aluminum’s unique properties—such as its lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity—make it an ideal material for manufacturing parts across various industries.
The significance of aluminum castings cannot be overstated. In the automotive industry, aluminum rims are used to reduce vehicle weight, which in turn improves fuel efficiency. In packaging, aluminum tins and cans offer durability and ease of recycling, contributing to sustainability efforts. Additionally, aluminum castings are vital in aerospace, where precision and lightweight properties are essential for aircraft performance.
To better understand why aluminum is the go-to material for casting, let’s break it down into its key benefits:
- Lightweight: Aluminum is much lighter than other metals like steel and iron, which makes it ideal for reducing overall weight in various applications, especially in the automotive and aerospace industries.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum’s natural oxide coating protects it from rust and corrosion, which is why it’s preferred for applications exposed to the elements, such as packaging and automotive components.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Aluminum casting processes, particularly die-casting, are highly efficient and cost-effective, making aluminum a popular choice in mass manufacturing.
Table 1: Key Benefits of Aluminum Castings
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Lightweight | Reduces overall weight in automotive and aerospace |
| Corrosion Resistance | Natural oxide coating protects against rust |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Efficient casting processes reduce manufacturing costs |
2. How are aluminum castings used in different industries?
Aluminum castings have widespread use in several industries. The automotive industry, packaging, and aerospace all benefit from aluminum’s versatility and high-performance properties. What’s the real story? The way aluminum casting improves efficiency, product quality, and performance is the true highlight.
- Automotive Industry: One of the most common uses for aluminum castings in the automotive industry is in the production of wheels or rims. Aluminum rims are lightweight yet strong, which helps improve fuel efficiency by reducing the overall weight of vehicles. Furthermore, aluminum castings are used in engine blocks, transmission housings, and other components that need to withstand high temperatures while maintaining strength.
- Packaging Industry: Aluminum castings are often used in the production of tins, cans, and other containers for food and beverages. The lightweight and durable nature of aluminum helps preserve contents while ensuring easy transportation and storage. In addition, aluminum’s recyclability adds an eco-friendly dimension to its use in packaging.
- Aerospace Industry: Aluminum castings are crucial in aerospace manufacturing, especially for parts such as airplane frames and engine components. The material’s light weight is critical for enhancing fuel efficiency in aircraft, while its durability and resistance to corrosion ensure long-lasting performance under extreme conditions.
The key takeaway here? Aluminum castings are indispensable to industries that rely on high-performance materials, durability, and cost-effective manufacturing.
Table 2: Common Uses of Aluminum Castings in Various Industries
| Industry | Application Example |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Wheels, engine blocks, transmission components |
| Packaging | Tins, cans, containers for food and beverages |
| Aerospace | Airplane frames, engine parts, structural components |
3. What is the process of making aluminum castings?
The aluminum casting process involves several steps, each designed to ensure that the final product meets high standards of quality and precision. Ready for the good part? The casting method you choose significantly impacts the performance of the final product, so let’s walk through the essential stages of aluminum casting.
- Melting the Aluminum: The first step in the casting process is to melt aluminum in a furnace. The aluminum is heated until it reaches a liquid state, typically around 660°C (1220°F). The molten aluminum is then ready to be poured into molds.
- Mold Creation: Molds can be made from various materials, including sand, metal, or graphite. The type of mold used depends on the casting method and the desired quality of the finished product.
- Pouring the Molten Aluminum: Once the mold is prepared, the molten aluminum is carefully poured into the mold cavity. This must be done swiftly and efficiently to prevent solidification before the mold is filled.
- Cooling and Solidification: After the molten aluminum is poured, it is allowed to cool and solidify. The cooling process can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the size and complexity of the casting.
- Finishing: Once the casting has cooled and solidified, the mold is removed, and the casting is cleaned and finished. This may include grinding, polishing, or machining to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
The casting process might sound simple, but there’s much more to it than just melting and pouring. Each step is crucial in determining the final product’s quality, which is why choosing the right casting technique is vital.
Table 3: Steps in Aluminum Casting
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Melting the Aluminum | Aluminum is heated to a liquid state |
| Mold Creation | Molds are made from sand, metal, or graphite |
| Pouring the Molten Aluminum | The liquid aluminum is poured into the mold |
| Cooling and Solidification | The aluminum solidifies in the mold |
| Finishing | The casting is cleaned and machined to meet specifications |
4. Why is aluminum preferred for casting?
Aluminum’s unique combination of properties makes it the go-to metal for casting in various industries. But here’s the kicker: It’s not just about the metal itself; it’s about how aluminum enhances product performance and longevity.
- Lightweight Properties: Aluminum is much lighter than other metals like steel, which is why it’s widely used in industries where weight is a critical factor. In the automotive and aerospace industries, reducing weight improves fuel efficiency, performance, and overall energy consumption.
- Corrosion Resistance: One of aluminum’s key advantages is its natural resistance to corrosion. Aluminum forms a protective oxide layer when exposed to air, which prevents it from rusting. This makes aluminum ideal for use in environments where parts will be exposed to moisture or harsh conditions.
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum has high thermal conductivity, meaning it can efficiently transfer heat. This is particularly important in automotive and aerospace applications where parts need to operate in high-temperature environments without losing structural integrity.
The versatility and performance advantages of aluminum make it the material of choice for casting, especially in industries that demand lightweight, durable, and cost-effective solutions.
Table 4: Advantages of Aluminum for Casting
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Lightweight | Reduces overall weight in automotive and aerospace |
| Corrosion Resistance | Protects against rust and corrosion |
| Thermal Conductivity | Efficient heat transfer in high-temperature settings |
5. How do aluminum castings impact the automotive industry?
Aluminum castings have revolutionized the automotive industry by providing lightweight yet durable components. What’s the real story? The ability to reduce vehicle weight without sacrificing strength has made aluminum a staple in modern car manufacturing.
- Rims and Wheels: Aluminum castings are widely used in the production of rims and wheels. Not only do they reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, but they also offer superior strength and resistance to corrosion. This results in better fuel efficiency, improved handling, and longer-lasting components.
- Engine Components: Aluminum castings are used in engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission housings. The material’s thermal conductivity helps dissipate heat, preventing engine parts from overheating. Aluminum’s lightweight nature also contributes to faster acceleration and improved overall vehicle performance.
- Chassis and Body Parts: Aluminum is increasingly used in vehicle chassis and body parts due to its strength-to-weight ratio. Automakers are adopting aluminum in place of steel for parts like doors, hoods, and trunk lids. This shift helps reduce the vehicle’s overall weight, contributing to better fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
What’s the key takeaway here? Aluminum castings are essential to modern automotive manufacturing. They reduce weight, improve performance, and contribute to a more sustainable automotive industry.
Table 5: Impact of Aluminum Castings on Automotive Industry
| Application | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Rims and Wheels | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, improved handling |
| Engine Components | Thermal conductivity, lightweight, enhanced performance |
| Chassis and Body | Reduced weight, improved fuel efficiency and emissions |
6. How do aluminum castings benefit the packaging industry?
Aluminum castings play a critical role in the packaging industry, particularly in the manufacturing of aluminum tins and cans used for food, beverages, and other products. Aluminum is the material of choice for packaging due to its strength, versatility, and recyclability. Ready for the good part? Aluminum packaging not only preserves product quality but also offers sustainable solutions that reduce environmental impact.
Aluminum packaging is lightweight, which reduces transportation costs and energy consumption. Its strength and ability to withstand various environmental conditions make it ideal for preserving the contents inside. Furthermore, aluminum provides an airtight seal that helps preserve the freshness and integrity of food and beverage products. As consumers increasingly demand eco-friendly packaging, aluminum stands out as a recyclable material, contributing to a circular economy where products are reused rather than discarded.
- Lightweight and Durable: Aluminum tins and cans are lightweight but durable, providing effective protection for contents while reducing transportation costs.
- Barrier Properties: Aluminum is an excellent barrier against light, oxygen, and moisture, helping to preserve the taste, quality, and shelf life of packaged goods.
- Recyclability: Aluminum is 100% recyclable, and its recycling process uses only a fraction of the energy required for primary production, making it an environmentally sustainable option.
The key takeaway? Aluminum castings provide reliable and sustainable packaging solutions for a variety of industries, offering benefits in terms of product preservation, cost savings, and environmental impact.
Table 6: Benefits of Aluminum in Packaging
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Lightweight | Reduces transportation costs and energy consumption |
| Barrier Properties | Protects against light, oxygen, and moisture |
| Recyclability | 100% recyclable, contributing to sustainability |
7. What are the challenges faced in aluminum casting for the aerospace industry?
Aluminum casting is crucial in the aerospace industry, where precision and strength are paramount. But here’s the kicker: the challenges faced in casting components for aerospace applications are significant. Aluminum castings used in aircraft components must meet strict requirements for both performance and safety. Let’s explore the unique obstacles manufacturers face when casting for aerospace applications.
- Precision Requirements: Aerospace components require very precise dimensions and tolerances, as even small deviations can affect the performance of the aircraft. Aluminum castings used in aerospace must meet rigorous standards to ensure the components function correctly under extreme conditions.
- High-Temperature Resistance: Parts used in aerospace applications are often exposed to high temperatures and stresses. Aluminum’s natural heat resistance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of components like turbine blades and engine housings.
- Strength-to-Weight Ratio: In aerospace, reducing weight is a critical factor to improve fuel efficiency and performance. Aluminum castings are preferred because they offer a good balance between strength and lightweight properties.
The challenges faced in aerospace aluminum casting highlight the importance of quality control and precision in the casting process. Ensuring that components meet the required specifications is crucial for safety and performance.
Table 7: Challenges in Aerospace Aluminum Casting
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Precision Requirements | Aerospace parts require extremely precise dimensions |
| High-Temperature Resistance | Aluminum must withstand high temperatures and stresses |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Aluminum offers a balanced strength-to-weight ratio |
8. How is aluminum casting quality controlled?
Quality control is essential in aluminum casting to ensure that the final product meets the required standards for strength, durability, and performance. What’s the real story? The importance of quality control in aluminum casting cannot be overstated, especially in industries where component failure can lead to significant consequences. Let’s take a closer look at how aluminum casting quality is controlled.
- Casting Inspection: After the aluminum has been cast, the components undergo visual inspections to detect any obvious defects like cracks or porosity. For more detailed analysis, X-ray or ultrasonic testing may be used to detect internal flaws.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Precision measurements are taken to ensure that the final product meets the required dimensions. Tolerances are strictly controlled to ensure that each part fits properly and performs as intended.
- Mechanical Testing: Mechanical tests, such as tensile strength and impact resistance tests, are carried out to ensure that the casting has the necessary strength and durability for its intended application.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): NDT techniques, such as dye penetrant inspection and magnetic particle inspection, are used to detect surface and subsurface defects without damaging the component.
Effective quality control ensures that aluminum castings meet the specifications required for critical applications, such as automotive parts and aerospace components. By adhering to strict quality standards, manufacturers can produce reliable and high-performance castings.
Table 8: Common Quality Control Methods in Aluminum Casting
| Quality Control Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Casting Inspection | Visual and X-ray inspections to detect defects |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Precision measurements to ensure proper fit and function |
| Mechanical Testing | Tensile strength and impact resistance testing |
| Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) | Techniques to detect defects without damaging the part |
9. What are the environmental impacts of aluminum casting?
Aluminum casting is a resource-intensive process that involves energy consumption and emissions. But here’s the kicker: the environmental impact of aluminum casting is increasingly being addressed through technological innovations and recycling initiatives. Let’s examine the environmental considerations surrounding aluminum casting and how the industry is working toward sustainability.
- Energy Consumption: The process of melting aluminum requires significant amounts of energy, particularly when the metal is being extracted from ore. However, this impact is mitigated by the widespread use of recycled aluminum, which requires only a fraction of the energy compared to primary production.
- Recycling and Sustainability: Aluminum is one of the most recyclable materials, and the recycling process requires only about 5% of the energy used in primary production. As a result, the use of recycled aluminum in casting helps reduce the carbon footprint of the manufacturing process.
- Emissions: The casting process can produce emissions, particularly from the melting phase. However, advancements in furnace technology and emissions control systems have helped reduce the environmental impact of aluminum casting.
The move towards sustainable aluminum casting is gaining momentum, with many manufacturers adopting recycling initiatives and investing in energy-efficient technologies to reduce their carbon footprint.
Table 9: Environmental Impacts of Aluminum Casting
| Environmental Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | Melting aluminum requires significant energy |
| Recycling and Sustainability | Recycled aluminum uses less energy and reduces waste |
| Emissions | The casting process produces emissions, mitigated by new technologies |
10. What are the different types of aluminum alloys used in casting?
Aluminum alloys are tailored to specific applications, and the choice of alloy significantly affects the performance and characteristics of the final product. What’s the real story? The selection of aluminum alloy plays a crucial role in determining the strength, durability, and heat resistance of the casting.
- A356 Alloy: This is one of the most commonly used aluminum alloys for casting. It has excellent mechanical properties and is often used in automotive and aerospace applications. It’s known for its good corrosion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio.
- ADC12 Alloy: ADC12 is widely used in the automotive industry, particularly for making engine components and transmission parts. It is known for its excellent fluidity and ability to be cast into intricate shapes.
- A380 Alloy: A380 is used in die casting and is ideal for applications requiring high wear resistance and strength. It is often used for parts in the automotive and electronics industries.
- LM6 Alloy: LM6 is a high-strength, corrosion-resistant alloy often used for marine and outdoor applications. Its durability makes it ideal for parts exposed to harsh environments.
The choice of alloy depends on the intended use of the component and the specific performance characteristics required. Understanding the properties of each alloy is key to optimizing aluminum casting applications.
Table 10: Common Aluminum Alloys Used in Casting
| Alloy | Common Applications | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| A356 | Automotive, aerospace components | High strength, good corrosion resistance |
| ADC12 | Automotive engine components, transmission parts | Excellent fluidity, good castability |
| A380 | Die casting, automotive, electronics | High wear resistance, strength |
| LM6 | Marine, outdoor applications | High strength, corrosion resistance |
11. How does aluminum casting compare to other metals for casting purposes?
Aluminum casting has numerous advantages over other metals such as steel and iron. But here’s the kicker: while steel and iron have their benefits, aluminum’s unique properties give it an edge in certain applications. Let’s compare aluminum casting to other metals and see why aluminum is often the preferred choice.
- Weight Comparison: Aluminum is significantly lighter than steel and iron, which makes it ideal for industries where weight reduction is a critical factor, such as automotive and aerospace. Aluminum’s lightweight nature helps improve fuel efficiency and performance.
- Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Although aluminum is lighter than steel, it offers a higher strength-to-weight ratio than iron, making it a strong yet lightweight material for casting.
- Corrosion Resistance: While steel can be prone to rust, aluminum naturally resists corrosion thanks to its oxide layer. This makes aluminum a superior choice for applications exposed to moisture and harsh environmental conditions.
What’s the key takeaway here? Aluminum casting provides a combination of lightweight properties, strength, and corrosion resistance that makes it the material of choice for a wide range of applications.
Table 11: Comparison of Aluminum Casting vs. Steel and Iron
| Property | Aluminum | Steel | Iron |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier | Heaviest |
| Strength-to-Weight | High | Moderate | Low |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Poor |
12. What innovations are shaping the future of aluminum casting?
The aluminum casting industry is continuously evolving, with innovations in technology and casting methods driving new possibilities. Ready for the good part? These advancements are making aluminum casting more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective than ever before.
- 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing is revolutionizing aluminum casting by enabling the creation of complex and customized parts with minimal material waste. Additive manufacturing allows for the rapid prototyping and production of intricate designs that were once impossible to achieve with traditional casting methods.
- Improved Casting Technologies: New technologies, such as high-pressure die casting and vacuum casting, are improving the quality and precision of aluminum castings. These advancements help produce castings with fewer defects and higher mechanical properties.
- Sustainability and Recycling: Innovations in aluminum recycling have made the casting process more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. The increased use of recycled aluminum helps reduce the carbon footprint of the industry.
What does the future hold? With the continued adoption of new technologies and sustainability practices, aluminum casting is poised for further growth and innovation, helping industries meet the demands of a changing world.
Table 12: Innovations in Aluminum Casting
| Innovation | Impact |
|---|---|
| 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing | Enables complex designs with minimal waste |
| Improved Casting Technologies | Higher precision and fewer defects |
| Sustainability and Recycling | Reduces energy consumption and environmental impact |
13. What are some notable examples of aluminum castings in real-world applications?
Aluminum castings are widely used in various industries, and many well-known companies rely on aluminum for their products. What’s the real story? The versatility and performance of aluminum castings are demonstrated by some of the most prominent companies and projects in the world.
- Automotive Industry: Major automotive manufacturers, such as Ford and General Motors, use aluminum castings in their vehicles to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency. Aluminum castings are used in engine blocks, wheels, and other critical parts.
- Aerospace Industry: Aerospace giants like Boeing and Airbus rely on aluminum castings for parts such as engine components and fuselage frames. The lightweight and durable properties of aluminum make it a key material in aircraft manufacturing.
- Consumer Electronics: Companies like Apple and Samsung use aluminum castings in their products, such as smartphones and laptops, to provide lightweight yet durable casings.
What’s the key takeaway? Aluminum castings have broad applications across industries, with companies from automotive to aerospace benefiting from the material’s performance and versatility.
Table 13: Notable Companies Using Aluminum Castings
| Company | Industry | Aluminum Casting Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ford | Automotive | Engine blocks, wheels, transmission parts |
| Boeing | Aerospace | Engine components, fuselage frames |
| Apple | Consumer Electronics | Smartphone and laptop casings |
14. How can businesses improve their aluminum casting operations?
Businesses can optimize their aluminum casting operations by focusing on improving processes, enhancing quality control, and adopting new technologies. But here’s the kicker: small changes can lead to significant improvements in efficiency, cost savings, and product quality.
- Investing in Technology: Upgrading to modern casting technologies, such as automated casting machines and high-pressure die casting, can improve precision, reduce waste, and increase overall production efficiency.
- Training and Skill Development: Ensuring that workers are properly trained in the latest casting techniques and quality control procedures can help prevent defects and ensure that products meet required specifications.
- Collaborating with Suppliers: Working closely with aluminum suppliers to secure high-quality raw materials can improve the overall quality of the casting and reduce defects. Strong supplier relationships also ensure that businesses can meet tight production schedules.
The key takeaway? Investing in technology, training, and supplier relationships can significantly improve the quality and efficiency of aluminum casting operations.
Table 14: Strategies for Improving Aluminum Casting Operations
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Investing in Technology | Upgrading casting machines and automation |
| Training and Skill Development | Educating workers on new casting techniques and QC |
| Collaborating with Suppliers | Building strong relationships with aluminum suppliers |
15. What is the future outlook for aluminum castings?
The future of aluminum casting looks bright, with continued demand across various industries and new innovations on the horizon. Ready for the good part? Aluminum casting will continue to play a crucial role in manufacturing, with growth driven by advancements in technology and sustainability efforts.
- Increased Demand: The demand for lightweight materials in the automotive and aerospace industries will drive continued growth in aluminum casting. As automakers and aircraft manufacturers strive to reduce weight and improve efficiency, aluminum casting will remain an essential part of the manufacturing process.
- Technological Advancements: With innovations such as 3D printing and additive manufacturing, aluminum casting will become even more efficient and cost-effective. These technologies will help create more complex and customized parts at lower costs.
- Sustainability Efforts: As environmental concerns grow, the aluminum casting industry will increasingly focus on sustainability. The recycling of aluminum and the development of energy-efficient casting processes will help reduce the carbon footprint of the industry.
What’s the key takeaway? The future of aluminum casting is promising, with growth driven by the need for lightweight materials, technological advancements, and sustainability efforts.
Table 15: Future Outlook for Aluminum Castings
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Increased Demand | Continued growth in automotive and aerospace sectors |
| Technological Advancements | 3D printing and additive manufacturing improving efficiency |
| Sustainability Efforts | Focus on recycling and energy-efficient processes |
FAQ Section
Q1: What is aluminum casting?
Aluminum casting is the process of pouring molten aluminum into a mold, where it cools and solidifies into a desired shape. It’s used to make components for industries like automotive, packaging, and aerospace.
Q2: How does the aluminum casting process work?
The aluminum casting process involves melting aluminum, creating a mold, pouring the molten aluminum into the mold, and allowing it to cool and solidify. The casting is then finished by removing the mold and machining the component.
Q3: Why is aluminum used for casting instead of other metals?
Aluminum is preferred for casting due to its lightweight properties, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It is cost-effective and ideal for applications in automotive, packaging, and aerospace industries.
Q4: How does aluminum casting contribute to the automotive industry?
Aluminum castings are used in automotive applications like rims, engine components, and body parts. They help reduce vehicle weight, improve fuel efficiency, and enhance overall performance.
Q5: What are the environmental benefits of aluminum casting?
Aluminum is highly recyclable, making it an eco-friendly option. Its use in products like packaging reduces waste, and its lightweight properties help improve fuel efficiency in vehicles and aircraft.




