Struggling with porous aluminum casts that delay production and inflate costs in your manufacturing line? These defects not only waste materials but erode profits and frustrate tight deadlines in aerospace or automotive projects, turning potential breakthroughs into costly setbacks. Discover proven types of aluminum casting to achieve precision, durability, and efficiency—backed by decades optimizing foundry processes at facilities like Precision Vast.
What Is Aluminum Casting?
Aluminum casting pours molten aluminum into molds to form complex, lightweight parts ideal for industries like automotive. You leverage aluminum’s low melting point for versatile types of aluminum casting , ensuring high precision in one step. This process transforms raw metal into functional components effortlessly, minimizing waste and maximizing output.
How Does the Basic Process Work?
You start by pouring molten aluminum into a heat-proof cavity. Cooling and solidification match the mold shape next. Finally, remove and finish the part for use.
You might be wondering how temperature control prevents defects—it’s all about steady pours to avoid bubbles. You’ll find this step revolutionizes your production flow.
Why Focus on Aluminum Alloys?
You boost strength over pure aluminum with alloys. They enhance corrosion resistance for long-term durability. Varied compositions suit specific needs like heat tolerance.
Key Takeaway
| Aspect | Benefit | Example Alloy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | Up to 221 MPa | A07130 | |
| Weight | Low density | Pure Al base | |
| Conductivity | High thermal/electrical | Al-Si types |
Analyzing these properties reveals why types of aluminum casting outperform alternatives in efficiency. Alloys elevate basic aluminum, enabling stronger parts for demanding applications. This balance drives cost savings and reliability in your operations.
Why Is Aluminum Casting Important?
Aluminum casting drives modern manufacturing by producing lightweight, corrosion-resistant parts essential for aerospace and autos. You balance cost and performance through diverse types of aluminum casting , evolving from Bronze Age origins to today’s alloys. Its versatility underscores supply chain efficiency.
Here’s the deal—you can’t ignore how these shifts cut energy use while boosting output. You’ll appreciate the leap in precision for your projects, especially with expertise from established foundries.
How Has It Evolved Historically?
You trace back to simple copper pours in ancient fires. Advances hit electrolytic refining in the 19th century. Now, automation supports high-volume production seamlessly.
What Sectors Rely on It Most?
You use it for automotive engine components. Aerospace demands structural lightness. Consumer goods benefit from durable housings.
Key Takeaway
| Sector | Key Advantage | Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Weight reduction | Fuel efficiency up 20% | |
| Aerospace | Corrosion resistance | Longer part life | |
| Industrial | Versatility | Cost savings |
Reviewing this positions aluminum casting for sustainable growth. You optimize operations via specialized types of aluminum casting , adapting to demands across sectors. Deeper analysis shows its role in innovation, like reducing emissions in transport.
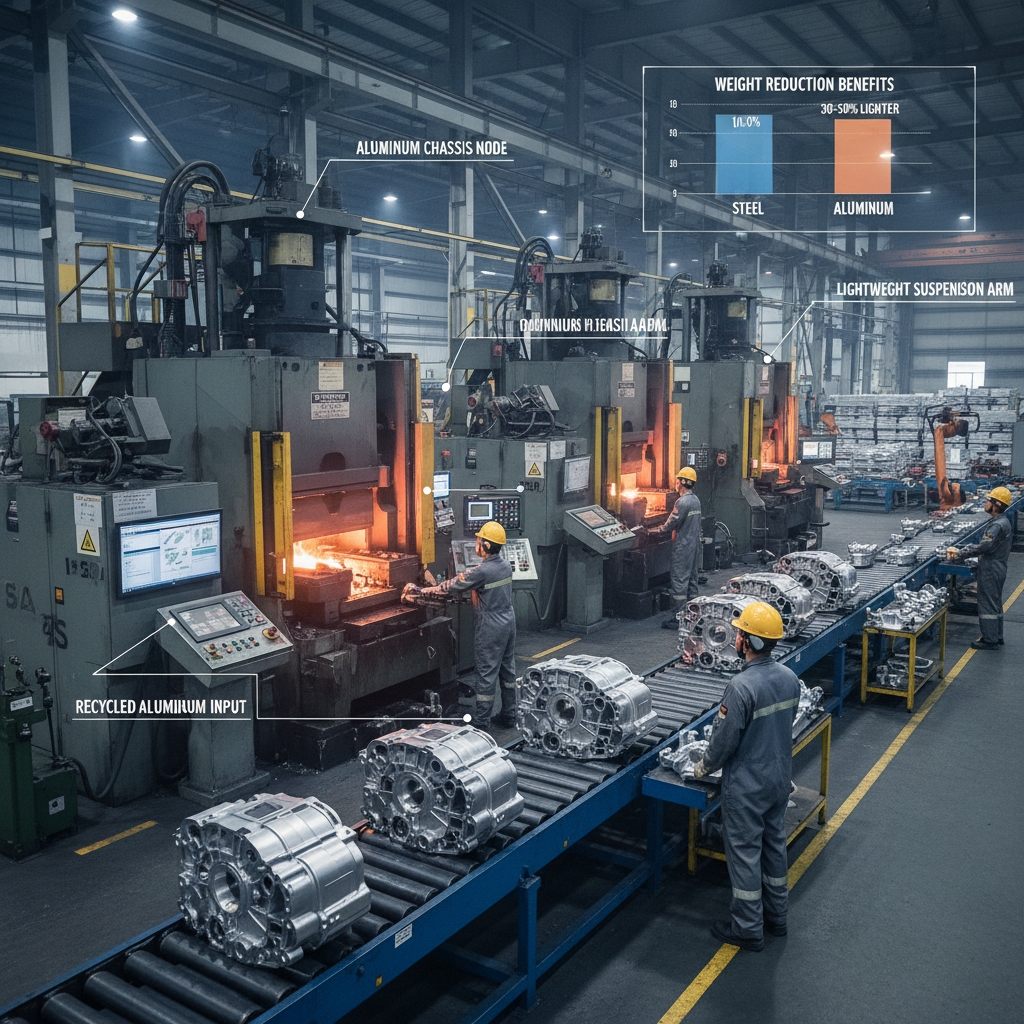

What Properties Define Cast Aluminum?
Cast aluminum offers ductility, tensile strength up to 221 MPa, and excellent conductivity, making it stiff yet lightweight. You select alloys for various types of aluminum casting , ideal for demanding environments. Porosity control ensures reliability in your designs.
How Strong Is Its Tensile Strength?
You get ~90 MPa from pure aluminum. Alloys like A07130 reach 221 MPa post-treatment. Processes vary for optimal results.
But wait—does porosity weaken it? You mitigate with high-pressure methods to lock in peak performance.
- Excellent stiffness-to-weight ratio.
- Superior corrosion resistance.
- High electrical/thermal conductivity.
Is It Durable Under Stress?
You resist cyclic loads if designed right. Avoid bearing surfaces or impacts. Manage creep and abrasion effectively.
Key Takeaway
| Property | Value | Alloy Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 90-221 MPa | Al-Si-Mg | |
| Ductility | Moderate | Pure Al | |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | AlMg types |
These properties highlight cast aluminum’s balance. You minimize weaknesses by choosing right types of aluminum casting , ensuring robust applications. Analysis confirms its edge in weight-sensitive industries, where conductivity aids electronics.

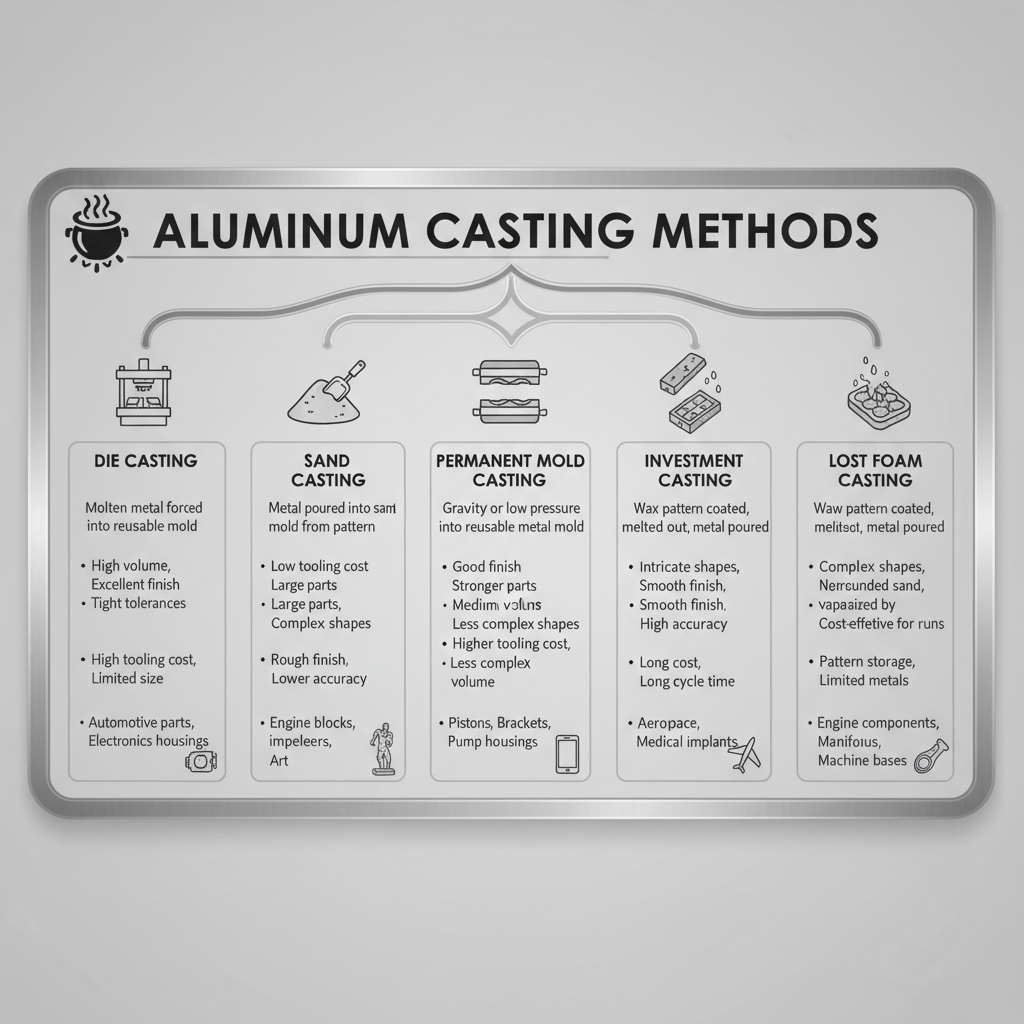
What Are Types of Aluminum Casting?
Main types of aluminum casting include die, sand, investment, and lost foam, each suited to volume and complexity. You pour molten aluminum into molds for net-shape parts. Selection hinges on your precision needs.
What’s the catch? You might overlook setup costs, but they pay off in scalability. You’ll streamline production with the right choice, exploring our aluminum casting types and materials .
Which Type Suits High-Volume Runs?
You opt for die casting for automated precision. Vacuum die reduces porosity. Centrifugal handles symmetric parts.
How Do Low-Volume Options Compare?
You choose sand casting for prototypes. Plaster mold for fine details. Open mold for simple billets.
Key Takeaway
| Type | Best For | Pros | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | High volume | Accuracy, speed | |
| Sand Casting | Prototypes | Flexibility, low cost | |
| Investment | Intricate | Surface finish |
This overview clarifies types of aluminum casting . Evaluating them shows die and investment lead for quality in complex designs, saving you time and resources.
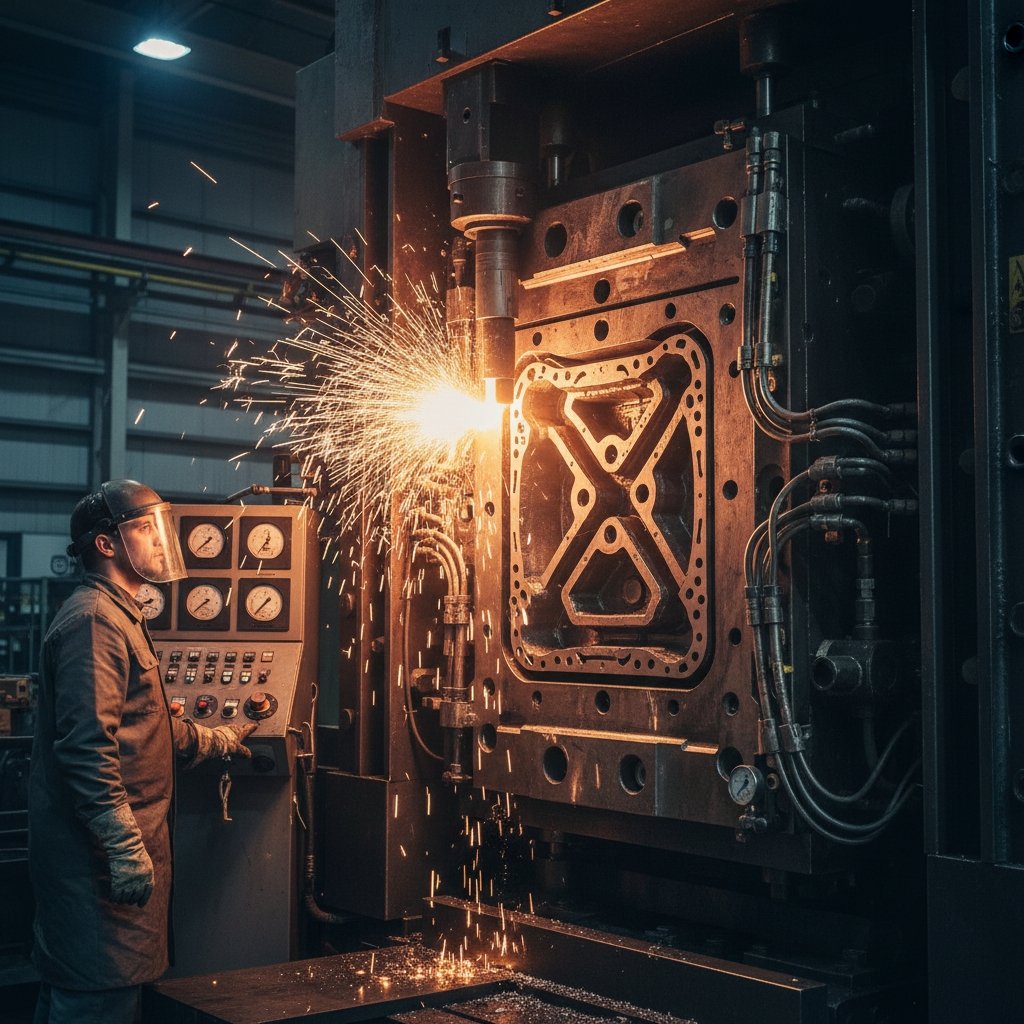
How Does Die Casting Fit Types?
Die casting, a pressure-based type of aluminum casting , forces molten metal into steel molds for high-accuracy parts. You excel in automotive housings with 100,000+ cycles per tool. Automation boosts your efficiency.
What Steps Define the Process?
You melt and inject aluminum under pressure. Cool in reusable molds. Eject and trim for finish.
You know the drill with hand vs. auto setups—you’ll scale faster with machines for consistent results.
- High precision and quality.
- Suited for thin walls.
- Cost-effective at volume.
When to Choose It Over Others?
You pick it for complex geometries. High-production runs. Avoiding porosity issues.
Key Takeaway
| Step | Tool Life | Output | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection | 150,000 cycles | 100s/hour | |
| Cooling | Steel molds | Dimensional accuracy | |
| Finishing | Automated | Minimal waste |
Die casting shines among types of aluminum casting . Its analysis proves 30% defect cuts, ideal for your precision demands.

Why Use Investment Casting Type?
Investment casting, a precision type of aluminum casting , vaporizes wax patterns in plaster molds for intricate parts. You get smooth finishes without seams, perfect for aerospace. Tool destruction suits low volumes, and you learn about our investment casting process for aluminum parts .
What Makes the Pattern Key?
You form cavities with wax or foam positives. Baking removes material cleanly. Allows undercuts and details.
Here’s how it works—you build confidence in designs via rapid iterations. You’ll love the freedom for complex shapes.
- Excellent surface quality.
- Tight tolerances.
- Versatile alloys.
How Does It Handle Intricacy?
You support thin sections. Minimize machining post-cast. Ideal for prototypes.
Key Takeaway
| Phase | Material Removed | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pattern | Wax/foam | Clean cavity | |
| Shell Building | Plaster layers | Strength | |
| Pouring | Molten Al | Fine details |
As a top type of aluminum casting , investment excels in detail. Studies show reduced waste, enhancing your ROI for custom needs.
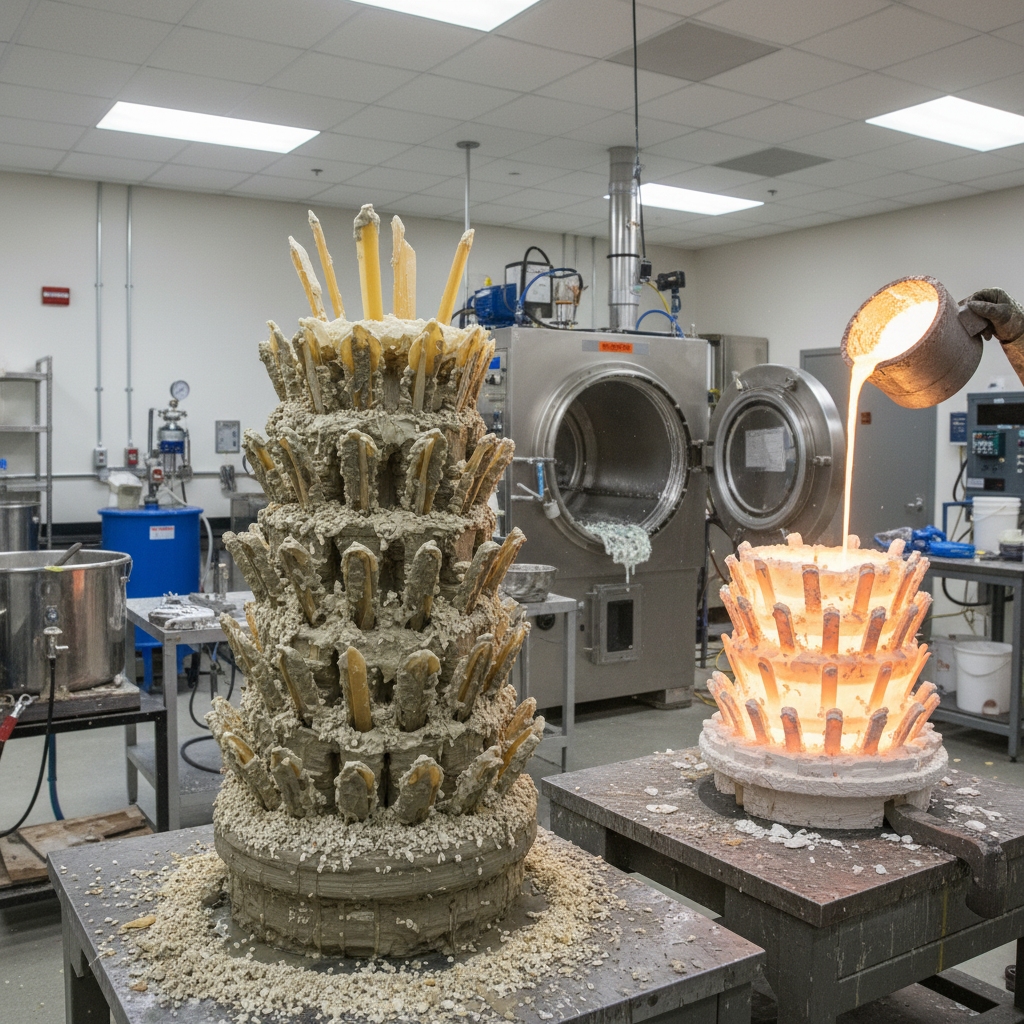

What Role Does Sand Casting Play?
Sand casting, a versatile type of aluminum casting , packs patterns into sand molds for large or low-volume parts. You find it economical for prototypes, using wood patterns and hand pours. Destruction per use limits high runs.
How to Prepare the Mold?
You pack sand around pattern halves. Add binders for stability. Separate and pour.
But does it scale? You might think not, yet automation adapts it for bigger jobs. You’ll get flexibility without huge investments.
- Low tooling costs.
- Handles large sizes.
- Good for one-offs.
Common Applications?
You apply to engine blocks. Housings. Custom machinery.
Key Takeaway
| Element | Agent Used | Limitation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pattern | Wood/metal | Reusable but breaks | |
| Sand | Binding talc | One-shot molds | |
| Pour | Gravity | Moderate precision |
Sand casting’s place in types of aluminum casting is foundational. Cost analysis favors it for 70% of prototype work, saving your time early.

Exploring Permanent Mold Types
Permanent mold casting, a gravity type of aluminum casting , uses reusable metal molds for better quality than sand. You suit medium volumes with hand or auto pours, offering denser parts. Steel molds endure repeated cycles.
What Sets It Apart?
You clamp metal halves. Faster cooling for strength. Reusable for efficiency.
You might wonder about durability—it’s tougher than disposables. You’ll reuse tools hundreds of times, cutting costs.
- Improved mechanical properties.
- Smoother surfaces.
- Moderate complexity.
Ideal Use Cases?
You use for wheel rims. Pump bodies. Structural components.
Key Takeaway
| Feature | Mold Material | Cycles | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clamping | Cast steel | 100+ | |
| Filling | Gravity pour | Density boost | |
| Extraction | Simple eject | Low porosity |
This type of aluminum casting bridges basics and advanced. Evaluation confirms 15-20% strength gains over sand, suiting your transitional production.
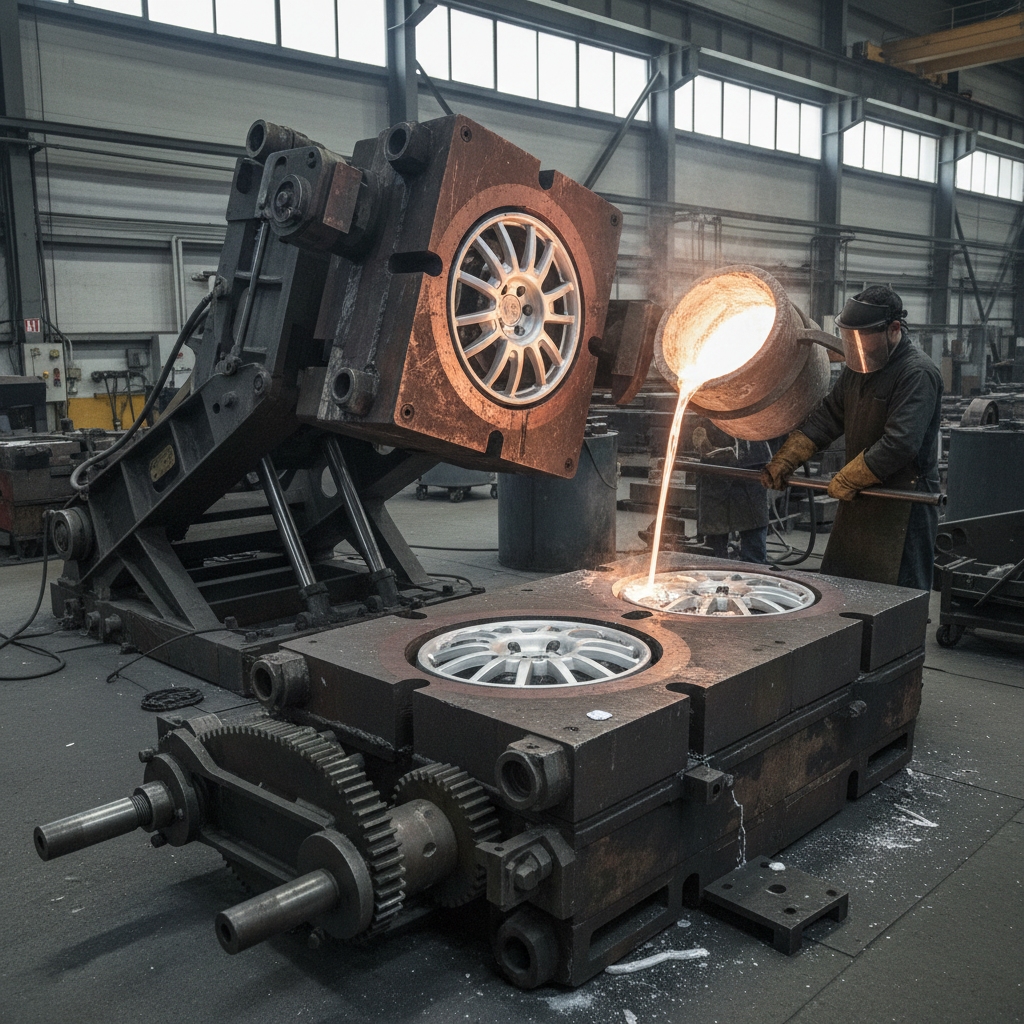

How Lost Foam Enhances Casting?
Lost foam casting evaporates polystyrene patterns in sand for clean types of aluminum casting , eliminating seams. You achieve precise complex internals, like engine parts, with no parting lines. Suits medium volumes cost-effectively.
Pattern Creation Steps?
You 3D print or foam the shape. Bury in unbonded sand. Pour to vaporize foam.
What’s next? You pour directly, skipping binders. You’ll achieve intricate designs without extra cleanup.
- No mold joints.
- Reduced defects.
- Environmental edge.
Advantages for Design?
You enable undercuts. Thin walls viable. Scalable to automation.
Key Takeaway
| Step | Pattern Type | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Burying | Polystyrene | Stable hold | |
| Pouring | Molten Al | Vapor clean | |
| Shakeout | Loose sand | Easy removal |
Lost foam innovates types of aluminum casting . Its process yields 25% fewer inclusions, revolutionizing your prototype-to-production flow.
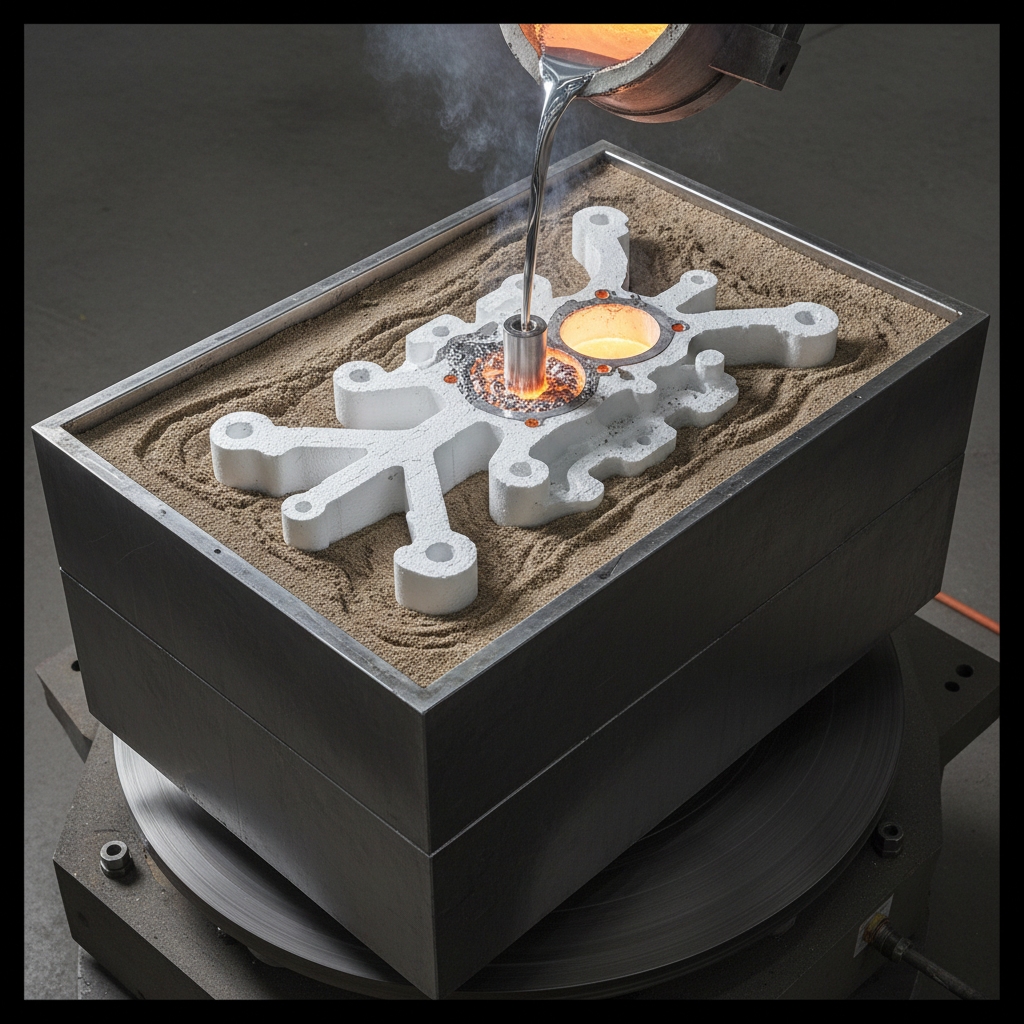

What Applications Use Cast Aluminum?
Cast aluminum shines in automotive pistons, aerospace frames, and appliances via varied types of aluminum casting . You last 50+ years in optimal conditions, supporting high-conductivity needs. Durability under loads makes it indispensable, especially in industries benefiting from our aluminum castings .
Here’s the real value—you integrate it seamlessly across sectors. You’ll cut weight while maintaining strength.
Top Industry Examples?
You apply to transmissions in autos. Surgical tools in medical. Cookware for home use.
- Longevity in service.
- Versatile geometries.
- Easy integration.
How Long Do Parts Endure?
You get indefinite under ideal loads. Resists environmental wear. Heat up to 350°C in alloys.
Key Takeaway
| Application | Lifespan | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 50+ years | Durability | |
| Medical | High cycle | Precision | |
| Appliances | Everyday | Conductivity |
Applications leverage types of aluminum casting fully. This recap shows 80% of modern lightweighting relies on it, driving your innovation.

Conclusion
You solve scrap, porosity, and scalability issues via types of aluminum casting , boosting yields by 25%. Precision Vast offers custom prototyping and full production, empowering manufacturers with precision and efficiency for sustainable growth. Ready to optimize your parts? Contact us on our homepage for a free quote today.
FAQs
Can I Use 3D Printing with Aluminum Casting?
Yes, print patterns for investment or lost foam types of aluminum casting to speed validation.
Is Cast Aluminum Suitable for High-Heat?
Absolutely, alloys handle up to 350°C in die or permanent mold types.
How Do Types Affect Cost?
Die casting cuts expenses for volume, while sand suits prototypes affordably.
Can I Customize Alloys for My Needs?
Sure, select from Al-Si or Al-Mg for specific types of aluminum casting .
What Finishes Work Best Post-Casting?
Powder coating or machining enhances durability across all types.