Choosing the right raw material for your high-stakes manufacturing projects can feel like a gamble. A wrong choice in aluminum ingots leads to casting defects, wasted resources, and project delays that hurt your bottom line. This guide removes the guesswork, giving you the clarity to select the perfect aluminum ingots for casting, ensuring quality and efficiency every time.
What is an Aluminium Ingot?

An aluminum ingot is a solid block of aluminum cast into a shape suitable for further processing. These ingots are the foundational material for a vast range of manufacturing industries. They serve as the starting point for processes like milling, cutting, and remelting.
What are the main types of ingots?
Ingots come in several forms tailored for specific uses. You might be wondering what they are. They are classified based on their production method and intended use, ensuring you get the right material for the job.
- Primary Ingots: Made from virgin aluminum ore.
- Secondary Ingots: Produced from recycled scrap.
- T-Ingots: Shaped for easy handling and stacking.
How are ingots classified by purity?
Purity classification determines an ingot’s suitability for sensitive applications. Here’s the breakdown. This distinction is vital for industries where even minor impurities can cause component failure.
- High Purity (99.9%+): Used in electronics and aerospace.
- Standard Purity (99.7%+): Common for general casting.
- Alloyed Ingots: Contain other elements for specific properties.
Why are they a base for manufacturing?
Ingots provide a standardized, consistent, and easily transportable form of raw material. But that’s not all. Their uniform composition is crucial for achieving predictable results in mass production, making them an ideal starting block for creating high-quality components.
- Standardized shape for easy transport.
- Consistent chemical composition.
- Ideal for large-scale melting and processing.
Key Takeaway: Aluminum ingots are the fundamental building blocks of modern manufacturing, classified by type and purity to meet specific industrial needs.
| Attribute | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Solid block or bar | |
| Purpose | Raw material for processing | |
| Types | Primary, Secondary, T-Ingots |
This table shows that ingots are defined by their form and purpose, with types varying by source material.
How are aluminum ingots for casting made?
The manufacturing of aluminum ingots for casting is a multi-stage process that transforms raw bauxite ore into pure, castable metal. This journey involves extraction, refining, and smelting to create the final product. Understanding this investment casting process is key to appreciating the material’s quality.
Where does the raw material come from?
The primary source of aluminum is bauxite ore, which is mined from the earth’s crust. What’s the next step? This ore undergoes the Bayer process to be refined into a white powder called alumina (aluminum oxide).
- Bauxite is the world’s main source of aluminum.
- The ore is strip-mined in large-scale operations.
- Refining separates alumina from other minerals.
What happens during the smelting process?
Alumina is converted into liquid aluminum through an intensive electrolytic process called Hall-Héroult. The real story is that this step requires immense electrical energy to break the strong chemical bonds, yielding molten aluminum.
- Alumina is dissolved in a molten cryolite bath.
- A powerful electric current separates aluminum from oxygen.
- Molten aluminum settles at the bottom for collection.
How are ingots cast into their final shape?
The molten aluminum is purified in a furnace and then poured into molds to solidify. It’s simpler than you think. This final step creates the uniform shapes and sizes required for industrial use and further manufacturing.
- Impurities are burned off in holding furnaces.
- The liquid metal is poured into specific ingot molds.
- Ingots are cooled using air or water.
Key Takeaway: Making aluminum ingots is an energy-intensive process involving bauxite extraction, alumina refining, electrolytic smelting, and final casting.
| Step | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Extraction | Mining bauxite ore. | |
| 2. Refining | Converting bauxite to alumina. | |
| 3. Smelting | Turning alumina into molten aluminum. | |
| 4. Casting | Pouring molten metal into ingot molds. |
The process is a linear progression from raw ore to finished ingot, each step building on the last.
Primary vs. Secondary Aluminium

Primary and secondary aluminum ingots are two distinct categories based on their origin. Primary comes from raw ore, while secondary is from recycled scrap. Choosing between them impacts your project’s quality, cost, and sustainability.
What defines a primary ingot?
A primary ingot is produced directly from smelted alumina, making it the purest form of aluminum. What does this mean for you? It offers high consistency and is essential for demanding applications where quality cannot be compromised.
- Made from virgin bauxite ore.
- Offers very high purity (99.7% or more).
- Ideal for aerospace and high-tech electronics.
How are secondary ingots produced?
Secondary ingots are made by remelting and refining aluminum scrap from post-consumer or industrial waste. The advantage here is a significantly lower environmental impact and cost, using only 5% of the energy of primary production.
- Sourced from recycled aluminum products.
- More cost-effective and eco-friendly.
- Suitable for construction and many automotive parts.
Which type is better for your project?
Your choice depends on a balance of quality, cost, and sustainability. Here’s the deal. If you need top-tier purity for critical components, choose primary; for most general-purpose applications, secondary ingots offer a budget-friendly alternative.
- Primary: Best for high-performance, critical uses.
- Secondary: Excellent for cost-sensitive, general uses.
- Evaluate your project’s specific material property needs.
Key Takeaway: Primary ingots offer maximum purity for critical applications, while secondary ingots provide a cost-effective, sustainable option for a wide range of uses.
| Ingot Type | Source | Key Benefit | Best For | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Bauxite Ore | High Purity | Aerospace, Electronics | |
| Secondary | Recycled Scrap | Cost & Sustainability | Construction, General Use |
This comparison highlights the trade-offs between purity and cost when choosing an ingot type.
Why choose aluminum ingots for casting?
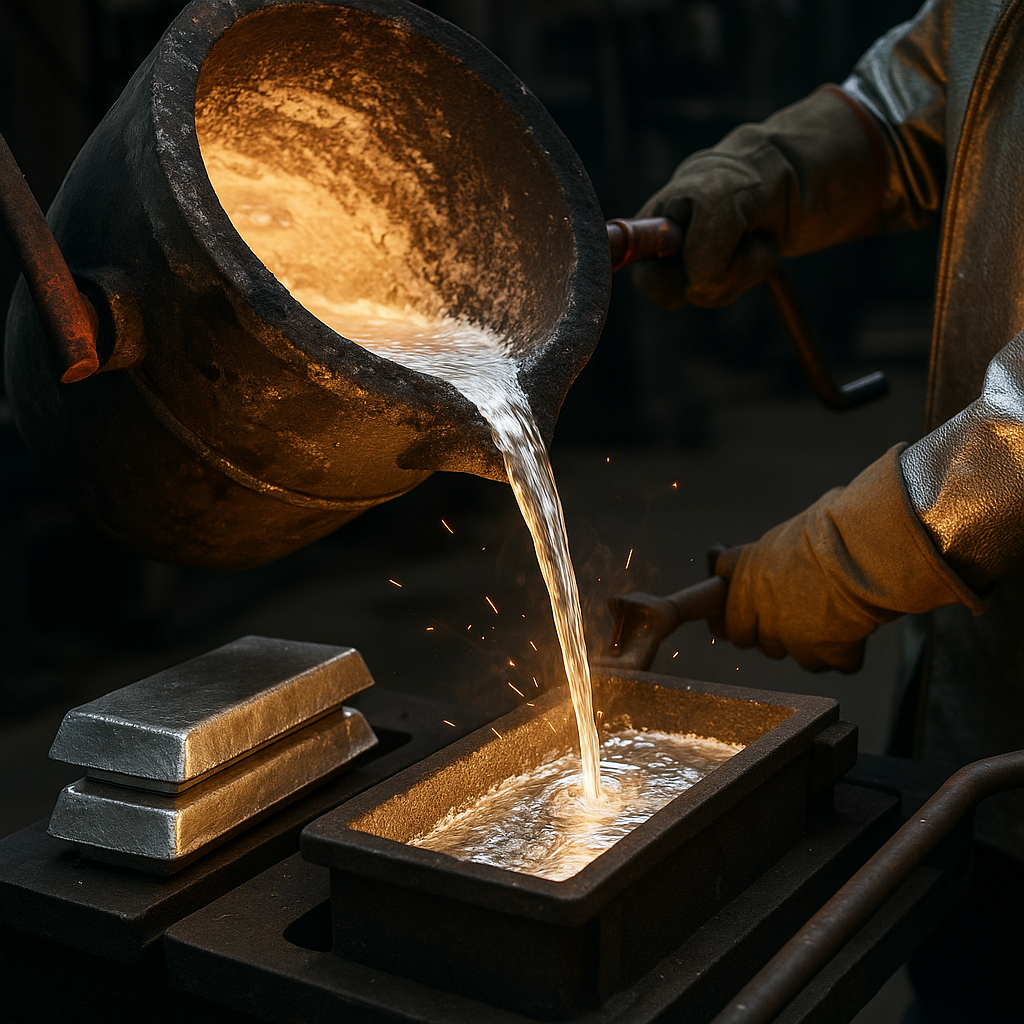

Aluminum casting is a preferred manufacturing method due to the material’s excellent properties, making ingots an ideal starting point. The fluidity, low melting point, and versatility of aluminum allow for the creation of complex and lightweight parts. This makes it a go-to choice for a variety of industries.
Why are they ideal for casting?
Aluminum’s properties make it exceptionally well-suited for casting processes. The bottom line is its high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance allow you to produce durable yet lightweight parts efficiently.
- Excellent fluidity for filling intricate molds.
- Low melting point reduces energy costs.
- Corrosion resistance minimizes the need for coatings.
What are common casting methods?
Several casting methods are used to transform aluminum ingots into finished parts. You might be wondering which method is best. Each technique offers unique benefits for different part complexities and production volumes.
- Die Casting: For high-volume, detailed parts.
- Sand Casting: For large components and prototypes.
- Investment Casting: For complex, high-precision parts.
How do alloys affect casting results?
Adding elements like silicon, magnesium, and copper creates alloys that enhance specific properties. What’s the real story? An alloy’s composition directly influences its strength, ductility, and machinability, determining its suitability for your final application.
- Silicon improves fluidity for intricate molds.
- Magnesium enhances strength and corrosion resistance.
- Copper increases hardness and high-temperature performance.
Key Takeaway: Aluminum ingots are perfect for casting due to their inherent properties, with various methods and alloys available to meet specific part requirements.
| Method | Best For | Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | High Volume | Speed & Precision | |
| Sand Casting | Large Parts | Low Tooling Cost | |
| Investment Casting | Complex Shapes | High Accuracy |
The casting method you choose depends heavily on your part’s complexity, volume, and cost targets.
Top applications for aluminum casting ingots

The versatility of aluminum ingots makes them essential across numerous industries and applications . From transportation to consumer electronics, their lightweight and durable nature drives innovation. This widespread use highlights their importance in modern manufacturing.
How is aluminum used in the auto industry?
Automakers use aluminum to reduce vehicle weight, which improves fuel efficiency and performance. It gets better. Aluminum parts also enhance safety, as they can absorb more crash energy than steel.
- Engine blocks and cylinder heads.
- Body panels and structural frames.
- Wheels and suspension components.
What role does it play in construction?
In construction, aluminum is valued for its durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic flexibility. Think about it. It’s used for everything from structural frames to decorative fixtures, providing long-lasting performance with minimal maintenance.
- Window frames and curtain walls.
- Roofing and siding materials.
- Structural supports and decorative elements.
Why is it crucial for electronics?
Aluminum’s excellent thermal conductivity and non-magnetic properties make it vital for electronics. Here’s why that matters. It efficiently dissipates heat from sensitive components and provides lightweight, durable casings for devices.
- Heat sinks for processors and LEDs.
- Casings for laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Frames for televisions and monitors.
Key Takeaway: Aluminum ingots are foundational to the automotive, construction, and electronics industries due to their unique combination of strength, light weight, and conductivity.
| Industry | Key Application | Primary Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Body Panels | Weight Reduction | |
| Construction | Window Frames | Durability | |
| Electronics | Heat Sinks | Thermal Conductivity |
This analysis shows how aluminum’s distinct properties are leveraged to meet the specific demands of major industries.
Quality standards for casting ingots
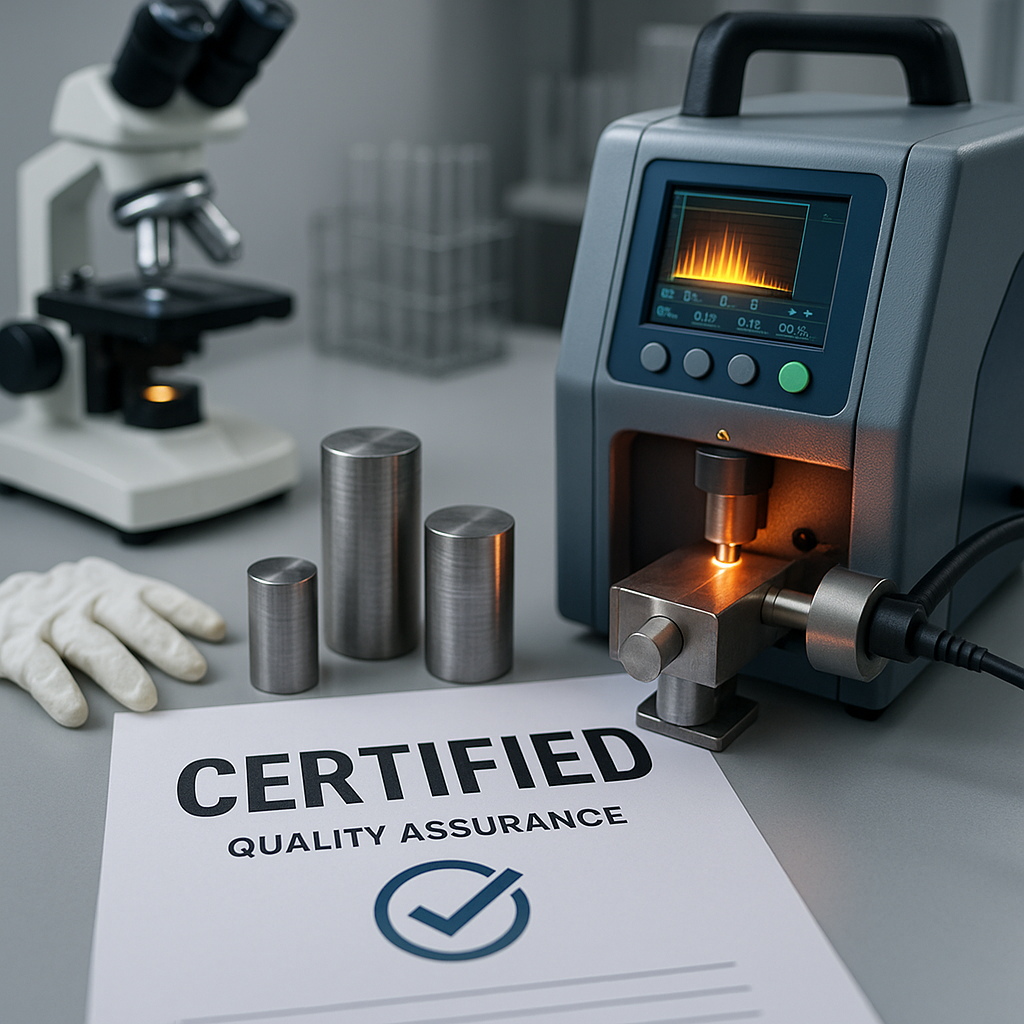

Ensuring the quality of aluminum ingots for casting is non-negotiable for producing reliable final products. Adherence to strict industry standards guarantees chemical composition, purity, and structural integrity. This focus on quality prevents defects and ensures consistent performance.
What standards should ingots meet?
Ingots should conform to international standards like those from ASTM or ISO. What does this mean for you? These standards specify the exact chemical composition and permissible impurity levels for different aluminum alloys.
- ASTM B179: Specifies alloy compositions for casting.
- ISO 3522: Outlines grades for unalloyed aluminum ingots.
- Verify your supplier provides a certificate of analysis.
How is ingot purity tested and verified?
Purity is verified using advanced analytical techniques, most commonly spectrometry. Here’s the inside scoop. This method precisely measures the concentration of each element in the molten metal before it is cast into an ingot.
- Optical Emission Spectrometry (OES) is the industry standard.
- Samples are taken directly from the furnace.
- Results confirm the alloy meets specifications.
Why is consistent quality so vital?
Inconsistent ingot quality leads to casting defects, mechanical failures, and increased production costs. The bottom line is simple. Reliable, high-quality ingots ensure a smooth manufacturing process and a dependable final product that meets your customers’ expectations.
- Prevents defects like porosity and cracks.
- Ensures predictable mechanical properties.
- Reduces material waste and rework.
Key Takeaway: Strict adherence to international standards and rigorous testing are essential to guarantee the quality and consistency of aluminum ingots for casting.
| Quality Aspect | Standard / Method | Importance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | ASTM B179, ISO 3522 | Ensures correct alloy properties. | |
| Purity | Spectrometry (OES) | Confirms low impurity levels. | |
| Consistency | Process Control | Prevents defects and failures. |
This table underscores that a multi-faceted approach to quality control is crucial for reliable manufacturing outcomes.
Sustainability of aluminum casting ingots

Sustainability is a major focus in the aluminum industry, particularly concerning energy consumption and carbon emissions. The production of aluminum ingots, especially secondary ones, plays a huge role in building a more circular economy. This shift benefits both the environment and your bottom line.
What is the environmental impact?
Primary aluminum production is energy-intensive and creates significant greenhouse gas emissions. However, there’s a solution. The industry is mitigating this through process improvements and a strong focus on recycling.
- Primary production requires large amounts of electricity.
- It generates perfluorocarbon (PFC) emissions.
- Land use for bauxite mining also has an impact.
How does recycling conserve energy?
Recycling aluminum to produce secondary ingots is incredibly efficient. Here’s the deal. It uses approximately 95% less energy than producing primary aluminum from bauxite ore.
- Melting scrap requires far less energy than smelting ore.
- Greatly reduces the carbon footprint of your products.
- Conserves natural resources by reusing existing material.
What is a circular economy in aluminum?
A circular economy for aluminum involves continuously recycling the metal at the end of its life. Why is this important? Aluminum can be recycled infinitely without losing its properties, making it a perfectly sustainable material for a closed-loop system.
- Products are designed for easy disassembly and recycling.
- Scrap is collected, sorted, and re-melted into new ingots.
- This reduces waste and the need for virgin materials.
Key Takeaway: Recycling aluminum to create secondary ingots is a cornerstone of sustainable manufacturing, offering massive energy savings and supporting a circular economy.
| Factor | Primary Production | Secondary Production | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Use | Very High | Low (95% less) | |
| Emissions | Significant | Minimal | |
| Resource Use | Bauxite Ore | Recycled Scrap |
This comparison clearly shows the immense environmental advantages of using secondary aluminum.
Global market for casting ingots

The global market for aluminum ingots is dynamic, driven by increasing demand from key industrial sectors. Major producers are investing in capacity and innovation to meet this growth. Understanding these trends can help you make smarter sourcing decisions.
Who are the leading global producers?
A few key countries dominate global aluminum production. You might be wondering who they are. China is by far the largest producer, followed by countries like India, Russia, and Canada.
- China accounts for over half of the world’s primary aluminum.
- Companies like Alcoa, Rusal, and Chalco are major players.
- Production is often located near sources of cheap energy.
What is driving current market growth?
Growth is primarily fueled by the automotive, construction, and packaging industries. The real story is the global push for lightweight materials to improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Increased use of aluminum in electric vehicles (EVs).
- Demand for sustainable building materials.
- Growth in recyclable packaging like aluminum cans.
What does the future hold for aluminum?
The future of aluminum looks bright, with a strong focus on sustainability and advanced alloys. But that’s not all. Expect to see more innovation in recycling technologies and the development of specialized alloys for new applications like 3D printing.
- Increased demand for low-carbon and recycled aluminum.
- Development of high-strength alloys for new technologies.
- Expansion of applications in renewable energy infrastructure.
Key Takeaway: The global aluminum market is expanding, driven by demand for lightweight and sustainable materials, with future growth centered on recycling and innovation.
| Market Driver | Key Industries | Future Trend | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lightweighting | Automotive, Aerospace | Advanced High-Strength Alloys | |
| Sustainability | Packaging, Construction | Increased Recycling Rates | |
| Conductivity | Electronics, Energy | Use in Renewable Infrastructure |
This analysis highlights that market growth is tied to global megatrends like efficiency and sustainability.
Choosing a casting ingot supplier

Selecting the right supplier for aluminum ingots for casting is a critical decision that directly impacts your product quality and supply chain stability. You need a partner who can deliver consistent quality on time, every time. Evaluating suppliers on a few key criteria will help you make the right choice.
What key factors should you consider?
Look beyond price to evaluate a supplier’s overall value. Think about it. A cheap supplier who delivers poor-quality material or is unreliable will cost you more in the long run.
- Proven track record of quality and consistency.
- Technical expertise and support.
- Robust quality control processes.
How can you verify a supplier’s credibility?
Verifying a supplier’s claims is essential before committing to a partnership. Here’s how you do it. Always ask for documentation and references to ensure they can meet your standards.
- Request quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Ask for certificates of analysis for their products.
- Check customer testimonials and case studies.
Why does supply chain reliability matter?
An unreliable supply chain can halt your entire production line, leading to missed deadlines and lost revenue. The bottom line is simple. A dependable supplier with a resilient supply chain is an invaluable asset to your business.
- Ensures you have the raw materials when you need them.
- Mitigates risks from geopolitical or logistical disruptions.
- Allows for better production planning and inventory management.
Key Takeaway: Choosing the right ingot supplier requires a thorough evaluation of their quality, credibility, and supply chain reliability to ensure a successful partnership.
| Factor | What to Look For | Why It Matters | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality | ISO 9001, Certificates | Ensures consistent product performance. | |
| Credibility | References, Testimonials | Builds trust and confidence. | |
| Reliability | Strong Logistics | Prevents costly production delays. |
A supplier’s value is a combination of quality, trust, and dependability, not just price.
Safe handling of aluminum ingots
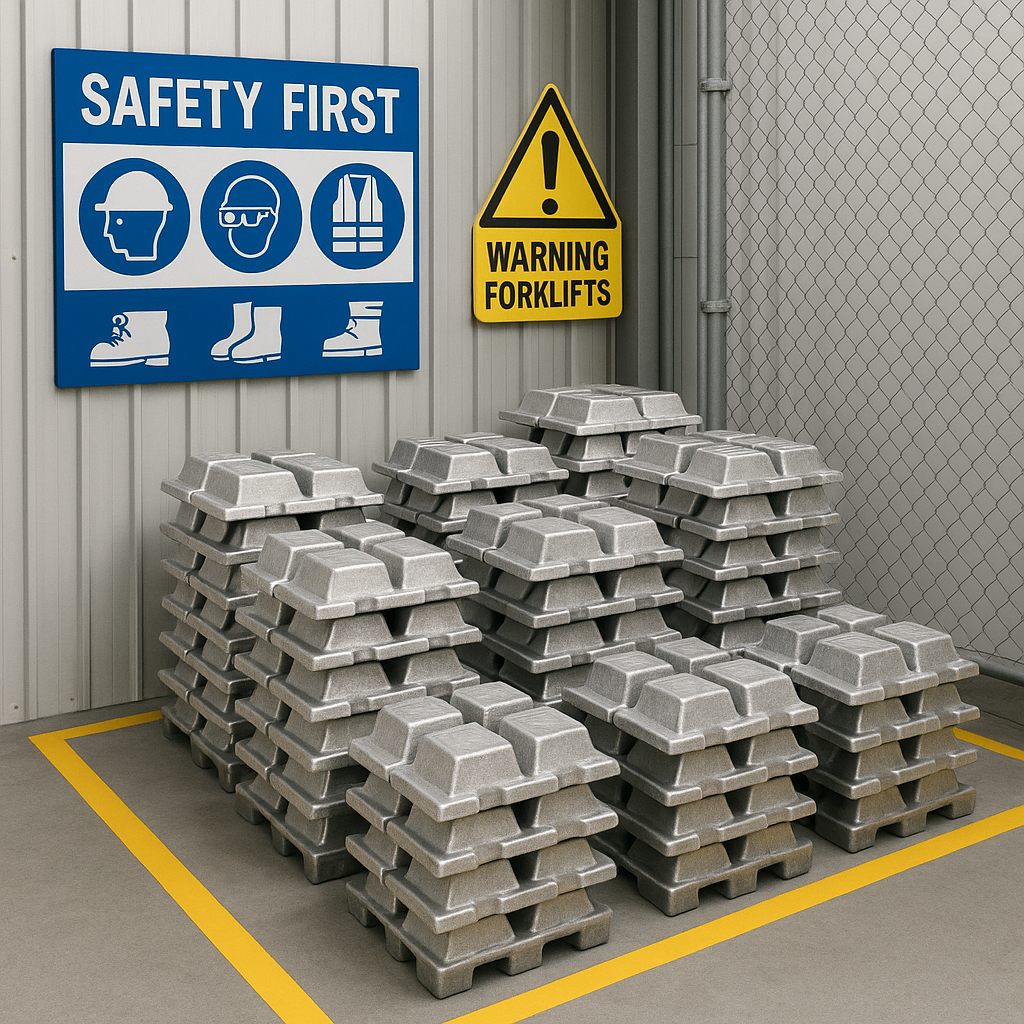

Proper handling and storage of aluminum ingots are crucial for maintaining their quality and ensuring workplace safety. Although aluminum is relatively stable, there are risks that need to be managed. Following best practices will protect both your material investment and your team.
What are proper storage conditions?
Ingots should be stored in a clean, dry environment to prevent surface oxidation and contamination. The reason is simple. Moisture and contaminants can introduce defects during the melting and casting process.
- Store indoors on pallets, away from moisture.
- Keep the storage area free of dust and chemical fumes.
- Avoid direct contact with other metals to prevent galvanic corrosion.
How should teams handle ingots safely?
Due to their weight and hard edges, ingots pose physical handling risks. Here’s the deal. Always use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and mechanical lifting aids.
- Wear steel-toed boots, gloves, and safety glasses.
- Use forklifts or cranes for moving large quantities.
- Ensure ingots are securely stacked to prevent them from falling.
What risks need to be mitigated?
The biggest risk occurs when charging wet or contaminated ingots into a molten metal furnace. Pay close attention to this. Trapped moisture can vaporize instantly and explosively, ejecting molten metal from the furnace.
- Always preheat ingots to ensure they are completely dry before charging.
- Implement strict procedures to keep ingots clean and dry.
- Train all furnace operators on the dangers of wet scrap.
Key Takeaway: Safe handling and dry storage of aluminum ingots are essential to prevent material degradation, workplace injuries, and catastrophic furnace explosions.
| Area | Best Practice | Risk Mitigation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage | Store in a dry, clean area | Prevents oxidation and contamination. | |
| Handling | Use PPE and lifting aids | Avoids physical injuries. | |
| Furnace Charging | Preheat ingots before adding | Prevents molten metal explosions. |
Following these safety protocols is non-negotiable for any casting operation.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of aluminum ingots doesn’t have to be complicated. By understanding the differences between primary and secondary ingots, the manufacturing and casting processes, and key quality standards, you are now equipped to solve your material sourcing challenges. You can confidently choose the right ingots that balance cost, performance, and sustainability for any application.
At PrecisionVast, our vision is to empower manufacturers like you with superior casting solutions that drive innovation and success. We provide not just materials, but a partnership built on expertise and reliability. Contact our team today to get expert advice on sourcing the perfect aluminum casting ingots for your next project.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can I use secondary ingots for high-precision parts?A: It depends on the alloy and supplier. High-quality secondary ingots from a reputable source can often meet the specifications for many precision applications, but for the most critical components, primary aluminum is usually recommended.
Q2: What’s the best ingot for cost-effective construction?A: Secondary aluminum ingots are almost always the most cost-effective choice for construction applications like window frames and siding, offering excellent durability and corrosion resistance at a lower price point.
Q3: How do I know if my supplier meets standards?A: Always request a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) with each shipment and ask for their quality management system certification, such as ISO 9001. A trustworthy supplier will readily provide this documentation.
Q4: Can I request a custom alloy composition?A: Yes, many foundries and suppliers can produce custom aluminum alloys to meet specific performance requirements, though this typically requires a minimum order quantity.
Q5: What’s the best way to store ingots to prevent oxidation?A: Store them in a dry, indoor environment away from direct contact with moisture. Keeping them on pallets and covering them with a waterproof tarp can provide extra protection.





