The secret weapon of investment casting -Applications and considerations for ceramic cores
The biggest feature of the investment casting process is the ability to manufacture complex shape and structure, difficult to use other processes to form a variety of metal parts.
However, in the casting production is still often encountered in the following situations, so that the casting engineers at their wits’ end.
- Casting cavity than the outer contour of the surface finish requirements are higher
- The inner cavity of the casting has a complex structure, or the inner cavity of the casting is larger than the mouth of the inner cavity, so it is not possible to make wax molds with wax mold molds.
- Small and deep holes inside the casting, or thin and long grooves, which can not be completed by 6-7 layers of shell making.
At this time, we need to use our secret weapon of investment casting – ceramic core.
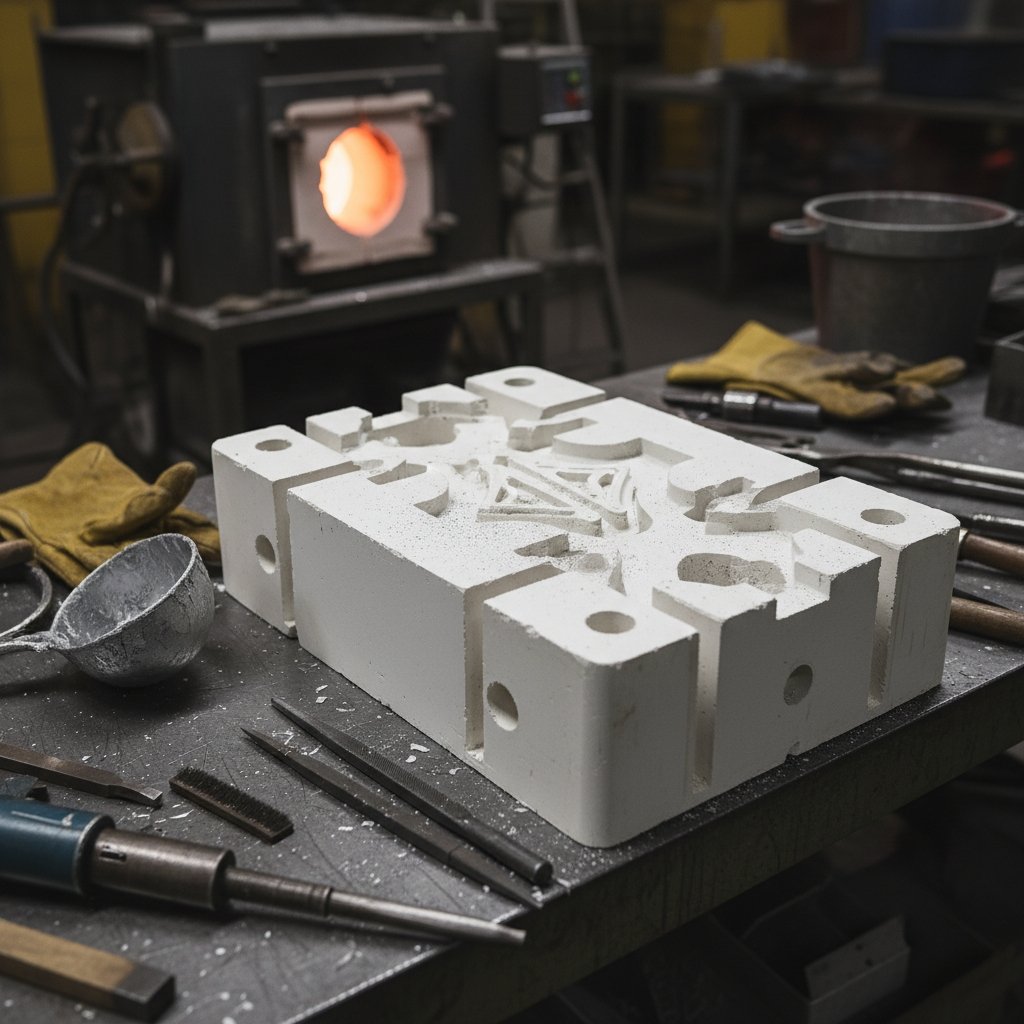
Ceramic core is a ceramic core used in investment casting process, as the formation of casting cavity of the transfer body, its role is: the formation of casting cavity structure, with the outer mold and mold shell to ensure that the casting of the cavity of the dimensional accuracy requirements. In layman’s terms, ceramic core is equivalent to the shell-making process completed in advance.
The production process of ceramic core casting is to put the ceramic core in the wax mold, inject wax, and then the wax mold cools down to form a wax mold with the ceramic core inside and the casting profile outside. The wax mold is then transferred to the normal process of tree formation and shell making, and the ceramic core inside the wax mold is equivalent to the shell making process that is completed in advance. In the picture below, the white color is the ceramic core and the red color is the wax mold.

In the video below, the gray ceramic core is the core and the red one is the wax mold.
Because of the special features of the ceramic core, it will end up in applications surrounded by high temperature liquid metals. Currently the most used metals are demanding stainless steels, iron-based, nickel- and cobalt-based alloys. Ceramic cores can withstand high temperatures when they are heated to 900-1050°C together with the casting mold after shell making, and are surrounded by liquid metal at 1500-1700°C during pouring, which is critical to ensure strength and dimensional stability. We Precisionvast casting in 20 years of casting production experience, stepped on the big and small ceramic core of the pit, serious caused by the batch of mold shell leakage of steel, but also caused a high rate of scrap, mostly because of the quality of ceramic core is not up to standard.
The following are the quality requirements and precautions for the use of ceramic cores
- High temperature stability, which includes high temperature strength and high temperature stability.
High-temperature strength refers to the ceramic core must have sufficient strength at high temperatures. This indicator is particularly long and thin ceramic core, must ensure that under the action of gravity does not deform, by the impact of steel does not deform, not displacement, not fracture, otherwise the casting is 100% scrap.
At the same time, but also to prevent high temperature ceramic core particles excessive sintering, resulting in a large number of ceramization and deformation, and ultimately after the casting to clean up these ceramic core is also very difficult, and even unable to clean up, resulting in castings scrapped.
High-temperature stability inspection method: because the ceramic core shape is different, the applicable metal materials are different, so there can not be a unified detection method. So the use of simulated metal casting ceramic core subjected to high-temperature state, will bake the qualified ceramic core according to its position in the casting, according to the casting heating temperature temperature, heat preservation, and then warmed up to the casting state temperature, and keep 2-4 minutes, unstable ceramic core will be seriously deformed. - Should not react with metal
- Ceramic cores do not outgas during casting, but should be distinguished from casting mold shells that outgas without baking. Do not react with the metal in the melt. To meet the above requirements, we must strictly control the ceramic core material and trace impurities in the material such as lead, zinc, iron, etc., and choose the material that does not react with metal.Solution for outgassing: Mold shells with ceramic cores will have porosity in the inner wall of the final casting due to lack of oxygen during roasting. The reason is that the ceramic core low-temperature reinforcing agent phenolic varnish reinforcement, baking, if the furnace lack of oxygen low-temperature reinforcing agent is not fully combusted to exclude the existence of the form of carbide, pouring will produce a lot of gas. The solution is to mold shell baking process, to high temperature, pull open the door for a few minutes, so that the furnace fully into the oxygen, you can avoid the production of casting porosity.3. Room temperature strengthRoom temperature strength refers to the strength of the ceramic core in the wax pressure, the reason why it is important, because in the production of wax molds must withstand the pressure of wax injection, room temperature ceramic core is generally more brittle, too much pressure will make it break. With lower pressures, the surface of the wax mold tends to shrink and concave. Increasing the roasting temperature increases the room temperature strength of the ceramic core, which also reduces the fracture, but brings great difficulties to the process of cleaning out the sand. In order to solve this performance, the surface of ceramic core is dipped and coated with phenolic varnish to improve the room temperature strength. The room temperature strength of the ceramic core can be increased by 3-4 times after dipping and coating, so that when the wax mold is pressed, as long as the core is placed properly, the ceramic core fracture defects are not easy to produce.In the picture below, the right side is the ceramic core, the left side is the casting, the internal cavity is empty, the internal cavity structure is the ceramic core structure, the center is red is the wax mold wrapped ceramic core.
- Coefficient of thermal expansion
The coefficient of thermal expansion should be low. As the ceramic core in the dewaxing, roasting and casting process, often rapid heating, so that the ceramic core is subjected to thermal shock, the ceramic core and mold shell expansion is different, the ceramic core in the mold shell inside, it is heated at different speeds, the ceramic core is often pre-burned, while the mold shell is still continuing to volatilize the water or chemical changes, and ultimately the ceramic core can be deformed, fracture. - Ceramic core removal
Ceramic core removal refers to the ceramic core from the casting is easy to remove. Removal must not damage the casting, which is also an important factor that must be considered when selecting the ceramic core material. The core is generally available chemical and mechanical methods, if the shape is simple, large size, the core material is corundum powder, available mechanical methods such as vibration tapping. Size small shape complex, core material is quartz glass tube or quartz glass powder, to remove the chemical method. - Surface roughness of ceramic core
The use of ceramic core to form the inner cavity of the parts, generally speaking, is able to achieve the drawings on the specified tolerance, the tolerance is plus or minus 0.3 mm.Finish generally up to Ra3.2-6.3
Some castings have a complex inner cavity structure, or the inner cavity of the casting is larger than the mouth of the inner cavity, so it is not possible to make a wax mold out of a wax mold. In such cases, foundries also use water-soluble wax cores or urea cores instead of ceramic cores. Water-soluble wax cores and urea cores as the name suggests are cores made of water-soluble wax and urea. These cores are put into wax molds, injected with wax, and pressed to form wax molds with water-soluble wax cores or urea cores inside, and then the wax molds are put into the water, and the water-soluble wax cores and urea cores inside are dissolved in the water, obtaining the internal structure of wax molds that could not be produced by the original molds.

The use of water-soluble wax cores or urea cores instead of ceramic cores is partly due to the low cost and partly due to the fact that the in-house shell making process in the foundry is more stable and consistent than the ceramic cores purchased from outsourcing.
However, due to the gradually increasing environmental protection requirements in recent years, the cost of treating wastewater from water-soluble waxes and urea cores has also increased, so the cost advantage is not able to close the gap with the cost of ceramic cores. For this reason, the popularity of water-soluble wax cores or urea cores has been limited.





