High-Pressure Die Casting has become one of the go-to methods for producing high-precision metal parts. However, it comes with both benefits and drawbacks that should be considered before choosing it for your manufacturing needs.
High-Pressure Die Casting allows for precision, efficiency, and speed, but it also has some limitations regarding material choices and cost-effectiveness. This process is widely used across multiple industries, but understanding the pros and cons can help you make a more informed decision.
Let’s explore the key advantages and disadvantages of High-Pressure Die Casting in greater detail.
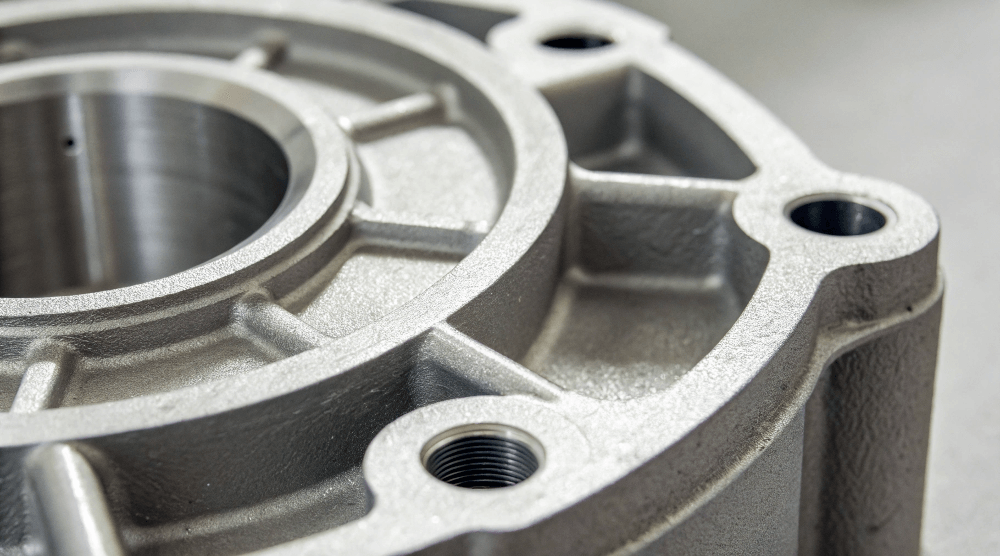
1. What is High-Pressure Die Casting?
High-Pressure Die Casting is a process where molten metal is injected into a mold under high pressure to form a solid casting. The process is known for producing high-quality, intricate parts with superior surface finishes and dimensional accuracy.
High-Pressure Die Casting involves injecting molten metal into molds under intense pressure, resulting in parts with excellent surface quality and precise dimensions. It’s a process used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
The process begins by melting metal, often aluminum or zinc, and injecting it into a steel mold under pressure. This pressure forces the metal to fill the cavity of the mold quickly, solidifying as it cools.
The key advantage of this process is its ability to produce complex shapes with tight tolerances. However, it does have some limitations that we’ll cover later.
Table: High-Pressure Die Casting Process Overview
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Metal Melting | Metal is heated until it melts into a liquid form. |
| 2. Injection | Molten metal is injected into the mold under high pressure. |
| 3. Cooling | Metal cools and solidifies inside the mold cavity. |
| 4. Ejection | The solidified part is ejected from the mold. |
2. What are the Key Advantages of High-Pressure Die Casting?
High Precision and Accuracy
High-Pressure Die Casting is one of the most precise casting methods available. It is ideal for producing parts that require high dimensional accuracy and consistency.
Precision and accuracy are the hallmark benefits of High-Pressure Die Casting. The process guarantees tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes, which are particularly essential in industries such as automotive and aerospace. These components can fit seamlessly into intricate designs, reducing the need for additional machining or modifications.
Table: Benefits of High Precision and Accuracy
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | Tighter tolerances and better fit for parts. |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, clean finish requiring less post-processing. |
| Consistency | High-volume production with minimal variation. |
High Production Efficiency and Speed
Another key benefit is the efficiency of the process. High-Pressure Die Casting can produce parts at a rapid pace, making it ideal for mass production. Once the initial mold is created, the casting process can be repeated quickly, reducing lead times and increasing output.
Efficiency and speed are crucial in modern manufacturing, and High-Pressure Die Casting offers both. This advantage helps companies reduce time-to-market, meet customer demand more efficiently, and keep costs lower in high-volume production environments.
Table: High Production Efficiency and Speed
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Cycle Time | Fast production cycle times increase efficiency. |
| Repeatability | High consistency in mass production. |
| Cost per Unit | Decreases significantly with high-volume production. |
Cost-Effectiveness for Mass Production
When it comes to mass production, High-Pressure Die Casting becomes highly cost-effective. Although the initial setup for molds can be expensive, the cost per unit decreases as production volume increases, making it a highly economical option for large production runs.
Cost-effectiveness is a major benefit, especially when considering long-term production volumes. Manufacturers can produce thousands of units at a fraction of the cost per unit, which can significantly boost profitability.
Table: Cost-Effectiveness in High-Pressure Die Casting
| Production Volume | Initial Setup Cost | Cost per Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Low Volume | High | High |
| Medium Volume | Medium | Medium |
| High Volume | Low | Low |
Excellent Surface Finish and Smooth Texture
High-Pressure Die Casting typically produces parts with an excellent surface finish. The high pressure used in the casting process helps create a smooth, uniform texture that requires minimal post-processing.
The smooth texture of the casting reduces the need for additional finishing processes. This not only saves time but also reduces additional labor costs and material waste, resulting in a more sustainable manufacturing process.
Table: Surface Finish Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Smooth Surface | High-quality, smooth surfaces with minimal defects. |
| Reduced Post-processing | Less need for finishing or extra treatments. |
| Time-Saving | Faster production with fewer finishing steps. |
3. What are the Main Disadvantages of High-Pressure Die Casting?
High Initial Setup Costs
The major downside of High-Pressure Die Casting is its high initial setup costs. Creating molds and setting up the machinery can be expensive, especially for small-scale production runs.
The high initial costs of mold creation and machine setup can be prohibitive for smaller manufacturers. While this method becomes more cost-effective with mass production, smaller production runs may not benefit from these advantages.
Table: High Initial Setup Costs
| Setup Factor | Cost Impact |
|---|---|
| Mold Creation | High one-time costs for designing and manufacturing molds. |
| Machine Setup | Significant investment in equipment and tooling. |
| Volume vs Cost | Higher costs for smaller production volumes. |
Limited to Certain Materials
High-Pressure Die Casting is typically limited to specific metals, such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. This limitation can be a drawback if you need to work with other materials or alloys for specialized applications.
Material limitations can hinder the versatility of High-Pressure Die Casting. If you need a casting made from a metal that doesn’t work well with the process, it may not be the right choice for your needs.
Table: Material Limitations in High-Pressure Die Casting
| Material Type | Suitability for High-Pressure Die Casting |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | Excellent |
| Zinc | Suitable for smaller, high-volume parts |
| Magnesium | Ideal for lightweight applications |
| Other Metals | Limited or unsuitable |
Potential for Defects such as Air Pockets
Despite its precision, High-Pressure Die Casting can sometimes result in defects like air pockets or porosity, especially when the mold is not properly designed or the metal is injected too quickly.
Defects are an inherent risk in many casting processes, including High-Pressure Die Casting. These imperfections can compromise the structural integrity of the final product, which may require additional quality control steps to rectify.
Table: Common Defects in High-Pressure Die Casting
| Defect | Cause |
|---|---|
| Porosity | Air trapped in the mold during injection. |
| Cold Shut | Metal solidifies before fully filling the mold. |
| Flash | Excess metal squeezed out from the mold. |
High Energy Consumption
High-Pressure Die Casting requires a significant amount of energy, particularly when heating the metal to its melting point and maintaining pressure during the injection process.
Energy consumption can make the process less environmentally friendly. High operational costs may arise from the energy-intensive nature of the process, impacting overall production costs.
Table: Energy Consumption in High-Pressure Die Casting
| Energy Requirement | Impact |
|---|---|
| Metal Melting | Requires significant energy to reach proper temperatures. |
| Injection Pressure | Energy needed to maintain pressure during the process. |
| Cooling | Power required for cooling systems during casting. |
Limitations in Casting Size
The size of parts that can be cast using High-Pressure Die Casting is limited by the size of the mold and the machine used. Larger parts may be difficult or even impossible to cast using this method.
Size limitations can restrict the use of High-Pressure Die Casting for certain applications. Larger, bulkier parts may require alternative casting or manufacturing methods.
Table: Size Limitations in High-Pressure Die Casting
| Part Size | Impact |
|---|---|
| Small Parts | Ideal for High-Pressure Die Casting |
| Medium Parts | Suitable, but requires careful mold design |
| Large Parts | May exceed mold and machine capabilities |
4. How Does High-Pressure Die Casting Work?
High-Pressure Die Casting involves a process where molten metal is injected into a mold under high pressure to produce intricate and high-precision parts. It is one of the most efficient casting methods for mass production, particularly for components requiring tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes.
The process begins by heating the metal to its melting point and injecting it into a steel mold under high pressure, ensuring that the mold fills completely and solidifies quickly. After the metal cools and solidifies, the mold opens to release the finished part. The high pressure forces the metal into even the most complex mold cavities, ensuring a highly detailed product.
Table: High-Pressure Die Casting Process Flow
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1: Metal Melting | Metal is heated to a molten state using high heat. |
| Step 2: Injection | Molten metal is injected into the mold at high pressure. |
| Step 3: Cooling | The metal solidifies inside the mold. |
| Step 4: Ejection | Finished part is ejected from the mold. |
The entire process is completed quickly, with each cycle producing one part. This is why it is an ideal method for mass production, where speed and precision are critical.
5. Which Materials are Used in High-Pressure Die Casting?
High-Pressure Die Casting is typically used with metals that have low melting points and good fluidity. The most common materials used in the process are aluminum, zinc, and magnesium due to their light weight, durability, and ability to withstand high temperatures.
The selection of material for die casting is crucial, as it affects the strength, weight, and thermal conductivity of the final product. Different alloys are chosen depending on the product’s needs, with aluminum being widely used in industries such as automotive and electronics for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio.
Table: Common Materials in High-Pressure Die Casting
| Material | Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight, strong, excellent corrosion resistance | Automotive, electronics, aerospace |
| Zinc | High strength, low melting point, good casting fluidity | Die-cast parts, hardware, toys |
| Magnesium | Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, good machinability | Aerospace, automotive, sporting equipment |
Each material offers specific benefits. For instance, aluminum is favored for its excellent performance in high-stress applications, while zinc is often used for lower-cost, smaller parts requiring less strength.
6. What Are the Benefits of High-Pressure Die Casting in Mass Production?
High-Pressure Die Casting is particularly advantageous when it comes to mass production. The process can produce a large number of parts in a short period, all with consistent quality and precision. This high production efficiency is one of the key reasons why industries that rely on high-volume manufacturing choose this method.
The benefits in mass production are clear: High-Pressure Die Casting provides fast turnaround times, cost savings through economies of scale, and high consistency across multiple parts. This is essential for industries such as automotive and consumer electronics, where speed and precision are critical.
Table: Mass Production Benefits of High-Pressure Die Casting
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Production Speed | Faster production cycles due to efficient processes. |
| Cost Reduction | Lower cost per part with increased production volume. |
| Consistency | Minimal variation between parts, ensuring uniform quality. |
| Reduced Waste | More precise molding reduces material waste. |
This method is an excellent choice for companies looking to produce high-quality components in large quantities, with minimal defects. The ability to streamline production processes also helps manufacturers meet tight deadlines and fulfill large orders quickly.
7. How Does High-Pressure Die Casting Compare to Other Casting Methods?
When it comes to choosing the right casting method for your project, it’s important to compare High-Pressure Die Casting to other methods like sand casting and investment casting. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best option depends on factors such as material, part complexity, and production volume.
High-Pressure Die Casting offers high precision and speed but can be limited in terms of material selection and part size. Other methods, such as investment casting, may be better suited for parts that require more complex shapes or materials that cannot be used in high-pressure systems.
Table: High-Pressure Die Casting vs Other Casting Methods
| Casting Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| High-Pressure Die Casting | High precision, fast production, low unit cost for large volumes | High setup costs, limited to certain materials, size limitations |
| Sand Casting | Can handle larger parts, flexible with material choice | Lower precision, rough surface finish, slower production |
| Investment Casting | Excellent for intricate designs, suitable for a wide range of materials | Slower production, higher costs for small runs, can be labor-intensive |
Each method has its own ideal use cases, depending on the specific needs of the project. High-Pressure Die Casting is optimal for mass production of high-precision parts, while investment casting may be more suitable for smaller, more complex designs.
8. How Does Die Casting Impact Product Design and Engineering?
Die casting plays a significant role in shaping product design and engineering. The ability to create highly detailed and precise components has made die casting essential for designing intricate parts with specific functional requirements. However, there are specific considerations when designing for high-pressure die casting to ensure the process yields the best results.
The design must accommodate the limitations and advantages of the die casting process, such as draft angles, wall thickness, and the complexity of the mold. These factors directly affect how well the mold fills, how the part is ejected, and how strong and functional the final product will be.
Table: Key Design Considerations for High-Pressure Die Casting
| Design Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Draft Angles | Angles on walls of the mold to aid in part ejection. |
| Wall Thickness | Consistent wall thickness for uniform metal flow. |
| Part Geometry | Avoid sharp corners or intricate features that could cause defects. |
| Ribs and Bosses | Use ribs and bosses to reinforce structure and maintain strength. |
| Material Flow | Design molds to ensure optimal metal flow without defects like porosity. |
A well-designed part will be both cost-effective to produce and function as intended. Factors like wall thickness and draft angles reduce the likelihood of defects and improve the speed and efficiency of the casting process.
9. What Industries Use High-Pressure Die Casting?
High-Pressure Die Casting is used across several industries that require precision and durability in their components. From automotive to medical devices, the process helps create parts that meet strict industry standards.
Industries that rely on high-quality, mass-produced parts often turn to High-Pressure Die Casting for its ability to deliver precise, consistent, and cost-effective products. The automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics industries are particularly notable users of this technology.
Table: Key Industries Using High-Pressure Die Casting
| Industry | Common Applications |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components, transmission parts, structural components |
| Aerospace | Aircraft parts, turbine blades, structural elements |
| Consumer Electronics | Housings for electronics, computer components |
| Medical Devices | Parts for diagnostic equipment, surgical instruments |
| Industrial Equipment | Hydraulic parts, pumps, compressors, and valves |
High-Pressure Die Casting’s ability to produce highly complex and durable parts makes it ideal for these demanding industries. It is especially effective in sectors where precision and high-volume production are critical.
10. How Does High-Pressure Die Casting Contribute to Sustainability?
As industries worldwide aim to reduce their environmental impact, High-Pressure Die Casting is becoming an important part of sustainable manufacturing. The process allows for better energy efficiency, material conservation, and waste reduction compared to other traditional manufacturing methods.
Energy-efficient processes and the use of recyclable materials contribute to making High-Pressure Die Casting an environmentally friendly option. Additionally, many manufacturers are adopting sustainable practices such as using recycled aluminum, which reduces the environmental impact of the casting process.
Table: Sustainability in High-Pressure Die Casting
| Sustainability Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Material Recycling | Use of recycled metals, especially aluminum, helps conserve resources. |
| Energy Efficiency | New technologies reduce energy consumption during casting. |
| Waste Reduction | Improved mold designs reduce metal waste, leading to a cleaner production process. |
| Eco-friendly Materials | Use of low-impact materials and coatings that do not harm the environment. |
By improving energy use and minimizing waste, High-Pressure Die Casting can contribute to a greener manufacturing process, supporting industries in their sustainability goals.
11. What Are the Costs Involved in High-Pressure Die Casting?
The costs of High-Pressure Die Casting can vary depending on several factors, such as the complexity of the part, the material used, and the scale of production. While the initial setup costs for tooling and equipment can be high, the process becomes more cost-effective with larger production volumes.
The total cost of High-Pressure Die Casting includes setup costs, production costs per unit, and maintenance expenses. Understanding these cost factors is crucial for businesses when evaluating whether High-Pressure Die Casting is the right choice for their manufacturing needs.
Table: Cost Breakdown of High-Pressure Die Casting
| Cost Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Tooling Costs | Initial mold and die creation cost. Higher for complex designs. |
| Production Costs | Cost per unit, which decreases with higher volumes. |
| Material Costs | Costs of the raw materials used for casting, typically aluminum, zinc, or magnesium. |
| Machine Maintenance | Ongoing costs for maintaining die casting machinery to ensure optimal performance. |
The efficiency of High-Pressure Die Casting becomes apparent in mass production, where the cost per unit drops significantly. However, smaller production runs or more complex parts may result in higher initial costs.
12. How Do You Prevent Common Defects in High-Pressure Die Casting?
Despite the many advantages of High-Pressure Die Casting, there are common defects that can occur during the process, including porosity, cold shuts, and flash. These defects can impact the integrity and functionality of the final part, leading to costly rework or rejected products.
To prevent defects, manufacturers must pay close attention to mold design, injection speed, and metal temperature. Implementing quality control measures throughout the casting process can help minimize the likelihood of these issues.
Table: Common Defects in High-Pressure Die Casting and How to Prevent Them
| Defect | Cause | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity | Trapped air or gas pockets in the mold. | Control metal injection speed and pressure; ensure proper venting in the mold. |
| Cold Shut | Incomplete fusion of metal during injection. | Ensure proper temperature control for the molten metal. |
| Flash | Excess metal that leaks from the mold cavity. | Tighten mold seams and reduce injection pressure. |
| Misruns | Molten metal does not completely fill the mold. | Adjust metal temperature and increase injection speed. |
| Surface Cracks | Rapid cooling or improper handling of the mold. | Gradually cool the mold and optimize injection speed. |
By carefully monitoring and adjusting these factors, manufacturers can significantly reduce defects, leading to higher quality and consistency in their die castings.
13. What Innovations are Shaping the Future of High-Pressure Die Casting?
As industries continue to demand higher performance and more complex parts, innovations in High-Pressure Die Casting are helping manufacturers meet these needs. Advances in die casting machinery, software, and material science are all contributing to improvements in speed, precision, and sustainability.
Innovations such as automated die casting machines, advanced simulation software, and the use of lightweight materials are transforming the industry. These developments enable manufacturers to produce more intricate and precise parts while also improving the efficiency and sustainability of the process.
Table: Innovations in High-Pressure Die Casting
| Innovation | Impact |
|---|---|
| Automation | Increased production speed, reduced human error, and improved consistency. |
| Simulation Software | Enhances mold design and metal flow analysis, leading to fewer defects. |
| 3D Printing for Tooling | Faster mold production, reducing setup times and costs. |
| Lightweight Materials | Introduction of advanced alloys that provide better strength-to-weight ratios. |
These innovations make the die casting process more flexible, cost-effective, and capable of producing high-quality parts at scale.
14. How to Choose the Right High-Pressure Die Casting Supplier?
Selecting the right supplier for High-Pressure Die Casting is crucial to ensuring the quality and success of your project. A reliable supplier will have a track record of producing high-quality parts, using advanced technologies, and meeting customer deadlines.
When choosing a supplier, you should evaluate their experience, technology, certifications, and ability to provide post-production services. A supplier who is transparent about their processes and capable of offering customized solutions will be essential for meeting your specific needs.
Table: Factors to Consider When Choosing a High-Pressure Die Casting Supplier
| Factor | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Experience | Experienced suppliers are more likely to deliver high-quality, defect-free parts. |
| Technology | Advanced machinery and software lead to more precise and efficient production. |
| Certifications | Ensure the supplier adheres to industry standards and quality controls. |
| Post-Production Support | Consider the availability of after-sales support, including quality assurance and troubleshooting. |
| Lead Time | A reliable supplier should meet your delivery deadlines consistently. |
By choosing the right supplier, you ensure that your High-Pressure Die Casting project will run smoothly and efficiently, resulting in high-quality products.
15. What are the Environmental Considerations for High-Pressure Die Casting?
As environmental sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in manufacturing, High-Pressure Die Casting is evolving to reduce its environmental footprint. The process can be energy-intensive and produce waste, but there are ways to minimize its impact through better material management and energy efficiency.
Environmental considerations in High-Pressure Die Casting include energy consumption, waste management, and the use of recyclable materials. Manufacturers are also exploring new ways to reduce emissions and improve the sustainability of the process.
Table: Environmental Considerations in High-Pressure Die Casting
| Consideration | Impact |
|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | The process can be energy-intensive, but advancements in machinery are reducing energy use. |
| Material Recycling | The use of recycled metals, particularly aluminum, reduces the environmental impact. |
| Emissions Control | Implementing technologies to reduce emissions during metal heating and cooling processes. |
| Waste Reduction | Improved mold designs and metal flow reduce material waste. |
By improving energy efficiency and using more sustainable materials, High-Pressure Die Casting can continue to meet industry demands while minimizing its environmental impact.
Conclusion
High-Pressure Die Casting is a valuable method for precision manufacturing, offering numerous benefits such as high precision, efficiency, and excellent surface finish. However, it’s not without its drawbacks, including high setup costs, material limitations, and potential defects. Understanding both the advantages and disadvantages will help you determine if High-Pressure Die Casting is the right choice for your next project.
FAQ Section
- Q1: What is High-Pressure Die Casting?
High-Pressure Die Casting is a manufacturing process where molten metal is injected into molds under high pressure to create precise and intricate parts. - Q2: How does High-Pressure Die Casting work?
In High-Pressure Die Casting, molten metal is injected into a steel mold at high pressure, where it solidifies to form a detailed and accurate part. - Q3: What materials are used in High-Pressure Die Casting?
The most commonly used materials are aluminum, zinc, and magnesium due to their lightweight and durability. - Q4: What are the advantages of High-Pressure Die Casting?
High-Pressure Die Casting offers high precision, fast production, cost-effectiveness for mass production, and excellent surface finishes. - Q5: What are the disadvantages of High-Pressure Die Casting?
The main drawbacks include high initial setup costs, material limitations, potential defects, high energy consumption, and size limitations for casting.

