Aluminum casting is a widely used manufacturing process that involves pouring molten aluminum into a mold to create a specific shape or part. This method is essential in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods, where precision and durability are crucial. In this guide, we will explore the aluminum casting process, its types, benefits, and how it compares to other materials. Whether you’re new to aluminum casting or looking to deepen your knowledge, you’ll find valuable insights in this comprehensive article.
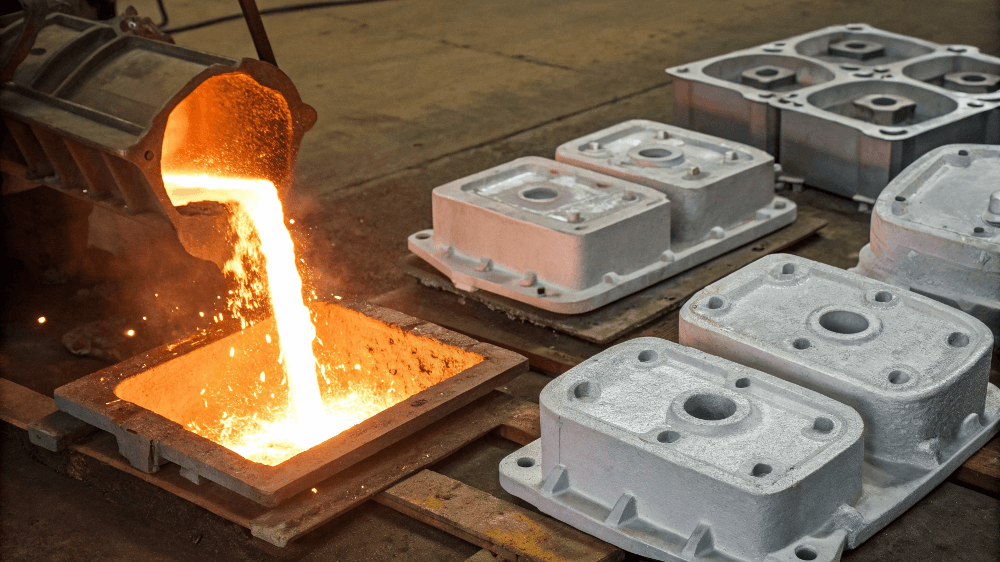
1. What is Aluminum Casting?
Aluminum casting is the process of shaping molten aluminum by pouring it into molds. The liquid metal solidifies in the mold to form a desired shape. This process is often chosen for its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision, which would be difficult or costly to achieve with other manufacturing methods. Aluminum’s unique properties, such as its lightweight nature, resistance to corrosion, and good conductivity, make it an ideal material for casting.
But here’s the kicker – aluminum casting isn’t just about pouring metal into molds. The process is more nuanced than that. It requires careful control over temperature, mold material, and the aluminum alloy used to ensure high-quality results. There are several types of aluminum casting processes, each suited for different applications. Some of the most common methods include sand casting, die casting, and investment casting. Understanding these methods and their benefits can help manufacturers select the best approach for their needs.
Table 1: Types of Aluminum Casting Methods
| Casting Method | Description | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Mold made from sand and binders | Low-volume production, large parts |
| Die Casting | Uses a metal die to inject molten aluminum | High-volume production, precision parts |
| Investment Casting | Uses a wax pattern and a ceramic mold | Complex, high-precision parts |
2. Why is Aluminum Casting Important?
Aluminum casting is essential for producing parts with a wide variety of characteristics, such as strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. The lightweight nature of aluminum allows manufacturers to create parts that reduce the overall weight of machinery or vehicles, which can improve energy efficiency and performance. Additionally, aluminum is highly resistant to corrosion, which extends the lifespan of the casted parts, making them ideal for use in industries like automotive and aerospace.
Ready for the good part? The significance of aluminum casting goes beyond just material properties. It also offers cost-effective solutions for producing large quantities of complex parts. Aluminum casting methods allow manufacturers to create intricate designs that would otherwise be expensive or impossible to produce with traditional machining methods. The versatility of aluminum casting enables it to be used in various industries, making it a critical component in manufacturing processes.
Table 2: Key Benefits of Aluminum Casting
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Lightweight | Reduces overall weight of machinery and vehicles |
| Corrosion Resistance | Ideal for use in harsh environments |
| Versatility | Suited for a variety of industrial applications |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Efficient for producing large quantities of parts |
3. How Does the Aluminum Casting Process Work?
The aluminum casting process involves several key steps. First, the aluminum alloy is melted in a furnace at high temperatures. The molten aluminum is then poured into a mold, which is typically made of sand, metal, or ceramic, depending on the casting method. Once the molten aluminum has cooled and solidified, the mold is removed to reveal the finished part.
This is where it gets interesting – the success of the aluminum casting process depends on factors like mold design, pouring temperature, and cooling rates. Any missteps in these areas can result in defects, such as porosity or shrinkage, which can affect the integrity and strength of the final product. For this reason, manufacturers must carefully control the casting environment to ensure high-quality results.
Table 3: Key Stages in the Aluminum Casting Process
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Melting | Aluminum alloy is melted in a furnace |
| Pouring | Molten aluminum is poured into the mold |
| Cooling | The molten aluminum solidifies in the mold |
| Mold Removal | The mold is removed to reveal the finished part |
4. What Are the Different Types of Aluminum Casting?
Aluminum casting can be performed using various methods, each suited to different types of projects. The most common methods include sand casting, die casting, and investment casting. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the volume, complexity, and precision required for the parts being produced.
What’s the real story? Each casting method offers unique benefits, which is why choosing the right one for your project is so important. For example, sand casting is ideal for low-volume production and large parts, while die casting is better suited for high-volume production of precision parts. Investment casting, on the other hand, is often used for creating highly intricate, high-precision parts.
Table 4: Comparison of Aluminum Casting Methods
| Casting Method | Production Volume | Precision | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Low to Medium | Moderate | Large parts, low-volume production |
| Die Casting | High | High | High-volume production, precise components |
| Investment Casting | Low to Medium | Very High | Complex, high-precision parts |
5. What Are the Key Benefits of Aluminum Casting?
Aluminum casting offers several advantages over other manufacturing methods. First, aluminum itself is a highly desirable material due to its strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and versatility. Cast aluminum parts can be used in a wide variety of applications, from automotive components to aerospace structures. But here’s the kicker – these benefits are only realized if the casting process is done correctly.
Aluminum casting also allows for intricate designs and complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with machining. This makes it ideal for producing custom parts or components with unique specifications. Furthermore, aluminum casting can be a cost-effective solution for producing parts in large quantities, making it a popular choice for industries looking to streamline production.
Table 5: Key Advantages of Aluminum Casting
| Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Lightweight | Ideal for reducing weight in vehicles and machinery |
| Corrosion Resistance | Suitable for harsh environments |
| Complex Geometries | Allows for intricate and detailed designs |
| Cost-Effective | Efficient for large-scale production |
6. How is Aluminum Casting Used in Various Industries?
Aluminum casting plays a crucial role in several key industries, offering unique properties such as strength, lightweight characteristics, and resistance to corrosion. These attributes make aluminum casting the preferred choice for producing high-performance components in industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.
So, what’s the real story? Aluminum casting is highly valued in the automotive industry for producing components like engine blocks, transmission cases, and structural parts. The lightweight nature of aluminum helps reduce the overall weight of vehicles, which in turn improves fuel efficiency and performance. Aluminum castings also offer excellent resistance to corrosion, ensuring that parts can withstand harsh operating environments, including exposure to moisture, heat, and chemicals. This combination of lightweight and durability makes aluminum casting ideal for automotive applications.
In the aerospace industry, aluminum casting is equally important. Aircraft and spacecraft parts are subject to extreme conditions, requiring materials that can withstand high temperatures, pressure, and stress. Aluminum castings meet these needs with ease, offering the perfect balance between weight reduction and high strength. Components such as turbine blades, structural frames, and engine parts often rely on aluminum casting to meet these stringent requirements.
But here’s the kicker – aluminum casting is also indispensable in the consumer electronics industry. The demand for lightweight yet durable enclosures for devices such as laptops, smartphones, and gaming consoles is constantly increasing. Aluminum castings provide a solution that meets both design and functional needs. With excellent thermal conductivity and an appealing finish, aluminum is frequently used to create housings that not only protect the internal components but also enhance the aesthetic appeal of the product.
What’s more? Aluminum casting is widely used in industrial equipment, marine applications, and even electrical components, where strength and resilience are key. The versatility of aluminum casting makes it an essential manufacturing method across multiple sectors, catering to both high-volume production and specialized, high-performance parts.
Table 6: Industries that Benefit from Aluminum Casting
| Industry | Common Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine blocks, transmission cases, structural parts | Lightweight, durable, corrosion-resistant |
| Aerospace | Aircraft frames, turbine blades, engine components | High strength, high temperature resistance |
| Consumer Electronics | Laptop enclosures, smartphone housings, gaming consoles | Lightweight, thermal conductivity, aesthetic finish |
| Industrial Equipment | Pumps, valves, gears, and machinery | Durability, strength, precision |
| Marine | Boat engines, propellers, offshore equipment | Corrosion resistance, strength |
Aluminum casting’s adaptability to different industries speaks to its incredible versatility. From enhancing performance in high-stress environments like aerospace and automotive, to providing sleek designs in consumer electronics, aluminum casting is a vital process that continues to evolve and meet the changing demands of various sectors.
7. What Materials are Best for Aluminum Casting?
When it comes to aluminum casting, choosing the right materials is critical for achieving high-quality results. Not all aluminum alloys are created equal, and the choice of alloy can significantly affect the mechanical properties, strength, and durability of the cast part. Commonly used alloys for aluminum casting include 300-series, 400-series, and 500-series alloys, each with its own specific applications and benefits.
Here’s the catch – the material selection for aluminum casting is a balancing act. You need to take into account factors such as the intended application of the part, the casting method, and the operating environment in which the part will function. For example, alloys like A356 and A380 are popular in automotive and aerospace industries due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and good castability. These alloys are often used in high-performance parts that require both strength and durability.
The key here is to carefully assess the needs of the final product. If the part will be exposed to high temperatures, you may want to use an alloy with higher heat resistance, such as 4032 or 4045. Similarly, if corrosion resistance is a priority, alloys like 6061, which have higher resistance to corrosion, may be ideal.
Table 7: Common Aluminum Alloys Used in Casting
| Alloy Type | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| A356 | High | Moderate | Automotive, aerospace components |
| A380 | Very High | Moderate | Die casting, complex shapes |
| 6061 | Moderate | Very High | Marine, structural applications |
| 4032 | Very High | High | High-performance automotive parts |
8. What Are the Common Defects in Aluminum Casting?
Aluminum casting, like any manufacturing process, comes with its own set of challenges, and defects can sometimes arise. The most common defects in aluminum casting include porosity, shrinkage, and cold shuts. Porosity occurs when gas bubbles are trapped within the casting, leading to holes or voids in the final part. Shrinkage, on the other hand, happens when the aluminum cools and contracts, resulting in dimensional inaccuracies.
But here’s the kicker – while defects are inevitable, they can often be minimized or prevented by controlling the casting environment. For example, controlling the temperature of the molten aluminum and ensuring that the mold is free from contaminants can help reduce porosity. Additionally, employing advanced simulation software can help predict and prevent shrinkage by optimizing the mold design and cooling rates.
Another defect that often occurs is cold shuts, which happen when the molten metal fails to fully fill the mold before cooling, leaving a visible seam. This can often be avoided by adjusting the pouring temperature or increasing the mold’s gating system to ensure better flow of the molten aluminum.
Table 8: Common Aluminum Casting Defects
| Defect Type | Description | Prevention Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity | Gas bubbles trapped within the casting | Control pouring speed and mold temperature |
| Shrinkage | Dimensional inaccuracies due to cooling | Optimize cooling rate and mold design |
| Cold Shut | Failure of molten metal to fill mold | Adjust pouring temperature and gating system |
9. How Do You Ensure Quality in Aluminum Casting?
Ensuring quality in aluminum casting is paramount for producing parts that meet industry standards and specifications. The quality of the final product can be affected by several factors, such as mold design, pouring technique, and alloy selection. So, what’s the secret to achieving consistent high-quality results?
One key factor is inspection. Manufacturers often use non-destructive testing methods such as X-ray or ultrasonic testing to identify any internal defects that might not be visible to the naked eye. This helps ensure that the part is free from issues like porosity or cracks that could compromise its performance. Additionally, it’s crucial to carry out dimensional inspections to ensure that the cast part meets the required specifications.
The other key component to ensuring quality is the control of the casting environment. Maintaining the right temperature for the molten aluminum, using high-quality molds, and controlling the cooling rate are all critical factors. This requires precision and expertise from the casting team to minimize defects and maximize the integrity of the final product.
Table 9: Methods of Ensuring Quality in Aluminum Casting
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Non-Destructive Testing | Techniques like X-ray or ultrasonic testing to detect internal defects |
| Dimensional Inspection | Checking the final part against specifications |
| Mold and Temperature Control | Ensuring molds are clean and controlling the temperature of molten aluminum |
10. What Are the Challenges in Aluminum Casting?
Aluminum casting, while effective, comes with its own set of challenges that manufacturers must address to ensure high-quality products. One of the biggest challenges is controlling the temperature of the molten aluminum. If the temperature is too high or too low, it can lead to defects such as porosity or shrinkage.
Another challenge faced by aluminum casters is the complex design of molds. Creating molds for intricate and detailed parts requires advanced technology and skilled labor. Additionally, molds must be durable enough to withstand multiple cycles of casting without degrading. This can increase production costs, especially for high-volume manufacturing runs.
What’s the real story? It’s not just about controlling the temperature and molds – it’s also about understanding the behavior of the aluminum during the casting process. Factors such as cooling rates and the placement of the molten aluminum can significantly affect the final product’s quality. This is why aluminum casting requires a deep understanding of metallurgy, mold design, and process control to overcome these challenges.
Table 10: Challenges in Aluminum Casting
| Challenge | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Difficult to maintain consistent temperature during pouring |
| Complex Mold Design | Requires advanced technology and skilled labor for intricate designs |
| Cooling Rate | Incorrect cooling can lead to shrinkage or defects |
11. How to Choose the Right Aluminum Casting Supplier?
Choosing the right aluminum casting supplier is crucial for ensuring the success of your project. When selecting a supplier, it’s essential to consider factors such as their experience with aluminum casting, the quality of their molds, and their ability to meet your production timelines.
Here’s the catch – don’t just focus on price. While cost is an important factor, the quality of the supplier’s work, their adherence to industry standards, and their customer service are just as important. It’s important to assess whether the supplier has experience in producing the specific type of casting you need, as different industries require different specifications.
Another key consideration is the supplier’s ability to provide a quick turnaround time without compromising quality. With aluminum casting, especially in industries like automotive or aerospace, timely delivery is critical. Make sure to ask for references or case studies to get a better understanding of the supplier’s capabilities.
Table 11: Factors to Consider When Choosing an Aluminum Casting Supplier
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Experience | Look for a supplier with experience in the specific type of casting needed |
| Quality Control | Ensure the supplier has robust quality control processes in place |
| Timely Delivery | Check the supplier’s ability to meet deadlines without sacrificing quality |
12. What Are the Cost Factors in Aluminum Casting?
The cost of aluminum casting is influenced by several factors, including the type of aluminum alloy used, the casting method, and the complexity of the part being produced. For instance, using a high-performance alloy will generally increase the cost of production, as these alloys are more expensive and require more precise control during the casting process.
Ready for the good part? The choice of casting method also plays a major role in determining costs. Die casting, for example, is more expensive than sand casting due to the need for specialized equipment and molds. However, for high-volume production runs, die casting can be more cost-effective in the long run due to its ability to produce large quantities of parts quickly and with high precision.
Table 12: Cost Factors in Aluminum Casting
| Cost Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloy | High-performance alloys increase material costs |
| Casting Method | Some methods, like die casting, require higher investment but may be more cost-effective for high-volume production |
| Part Complexity | More complex parts require advanced molds and increased production time |
13. How Do Aluminum Castings Compare to Other Metals?
Aluminum casting has distinct advantages over other metals, such as steel and iron. First, aluminum is much lighter than both steel and iron, making it an ideal choice for applications where weight is a concern, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
But here’s the kicker – aluminum also has superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for use in harsh environments where other metals may degrade over time. While steel and iron may offer greater strength, aluminum’s combination of strength, lightweight properties, and corrosion resistance gives it a unique edge in many applications.
Table 13: Comparison of Aluminum Casting vs. Steel and Iron
| Metal Type | Weight | Corrosion Resistance | Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Low | High | Moderate |
| Steel | High | Moderate | High |
| Iron | High | Low | Very High |
14. What Innovations Are Happening in Aluminum Casting?
The aluminum casting industry is not stagnant – innovations continue to improve the efficiency and precision of the casting process. One of the most exciting advancements is the development of 3D printing for mold creation. 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping and the creation of complex molds that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional methods.
Another innovation in aluminum casting is the integration of automation. Automated casting systems are being used to streamline the production process, reduce labor costs, and improve consistency. These systems can monitor the temperature and mold conditions in real time, making adjustments as necessary to ensure high-quality results.
Table 14: Innovations in Aluminum Casting
| Innovation | Description |
|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Allows for rapid prototyping and complex mold creation |
| Automation | Streamlines production, reduces labor costs, and improves consistency |
15. How Can You Improve the Aluminum Casting Process?
Improving the aluminum casting process involves optimizing several factors, including mold design, pouring technique, and cooling rates. One way to improve the process is by using advanced simulation software that can predict how the molten aluminum will behave in the mold. This can help manufacturers avoid common defects, such as porosity or shrinkage, before the casting even begins.
Additionally, adopting lean manufacturing principles can help improve the efficiency of the casting process. By reducing waste, improving material utilization, and streamlining workflows, manufacturers can reduce costs while maintaining high-quality standards.
Table 15: Ways to Improve the Aluminum Casting Process
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Simulation Software | Predict molten aluminum behavior to prevent defects |
| Lean Manufacturing | Optimize production by reducing waste and improving efficiency |
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve explored the ins and outs of aluminum casting, including the processes, materials, and benefits. We’ve also looked at the challenges and innovations that shape the future of aluminum casting. It’s clear that aluminum casting plays a vital role in many industries, from automotive to aerospace, offering significant advantages in terms of weight, strength, and corrosion resistance.
Choosing the right aluminum casting method, materials, and supplier can make all the difference in achieving high-quality results. By understanding the casting process and staying informed about new advancements, manufacturers can continue to innovate and improve their casting practices.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is aluminum casting?
Aluminum casting is the process of pouring molten aluminum into a mold to create specific shapes or parts. It is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods due to aluminum’s lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
Q2: How does the aluminum casting process work?
The aluminum casting process involves melting aluminum alloy, pouring it into a mold, and allowing it to cool and solidify. After cooling, the mold is removed, leaving a solid part.
Q3: What are the different types of aluminum casting?
The main types of aluminum casting are sand casting, die casting, and investment casting. Each method is suited for different applications depending on the volume and precision required.
Q4: What are the benefits of using aluminum for casting?
Aluminum casting provides several benefits, including lightweight, corrosion resistance, and the ability to produce complex geometries. It is also cost-effective for high-volume production.
Q5: How can I avoid defects in aluminum casting?
To avoid defects in aluminum casting, it is important to control the pouring temperature, mold design, and cooling rate. Proper inspection and quality control measures can also help identify and prevent defects early in the process.





